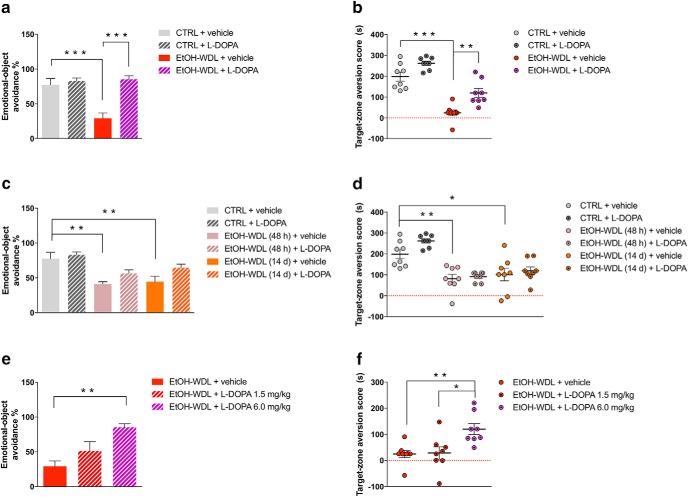
Figure 2.
Limbic memory disruption was rescued by l-DOPA/benserazide (l -DOPA) after 12 h withdrawal. Twelve hour alcohol-withdrawn rats administered with l-DOPA (EtOH-WDL + l -DOPA) displayed increased (a) emotional object avoidance and (b) target-zone aversion score with respect to 12 h alcohol-withdrawn rats receiving vehicle (EtOH-WDL + vehicle), up to alcohol-naive control (CTRL) rats' level. Limbic memory disruption was long lasting: alcohol-withdrawn rats showed decreased (c) emotional object avoidance and (d) target-zone aversion score following 48 h [EtOH-WDL (48 h)] and 14 d [EtOH-WDL (14 d)] of withdrawal. Long lasting limbic memory disruption in EtOH-withdrawn rats was not rescued by late stimulation of dopamine transmission. Preconditioning l-DOPA is not effective at significantly increasing (c) emotional object avoidance and (d) target-zone aversion score in EtOH-WDL (48 h) and EtOH-WDL (14 d) rats. In contrast, the rescuing effect of early (12 h withdrawal) l-DOPA administration was dose-dependent on both (e) emotional object avoidance and (f) target-zone aversion score. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM; n = 8 rats. ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05.