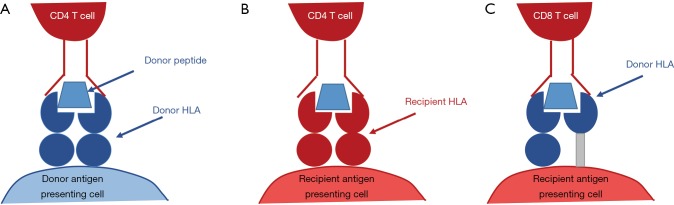
Figure 3.
Allorecognition pathways. (A) In direct allorecognition, the foreign HLA-peptide complex on a donor antigen presenting cell is recognised as non-self by the recipient CD4 T cell. The donor antigen presenting cell is then activate recipient CD8 T cells. This occurs in the early period following transplantation prior to the depletion of donor antigen presenting cells and is the basis of acute cellular rejection; (B) in indirect allorecognition, a donor allopeptide has been phagocytosed by a recipient antigen presenting cell and is presented to the CD4 T cell on self HLA class II. This process forms the basis of chronic rejection by establishing T cell help for de novo allo-specific CD8 T cells; (C) in semi-direct allorecognition, an intact donor HLA class I-peptide complex is incorporated into the membrane of a recipient antigen presenting cell by direct cell to cell contact or exocytosis. The simultaneous presentation of donor peptides to CD4 T cells on the antigen presenting cell’s HLA class II allows allo-specific CD8 T cell receiving cognate help from allo-specific CD4 T cell. HLA, human leukocyte antigen.