Fig. 4.
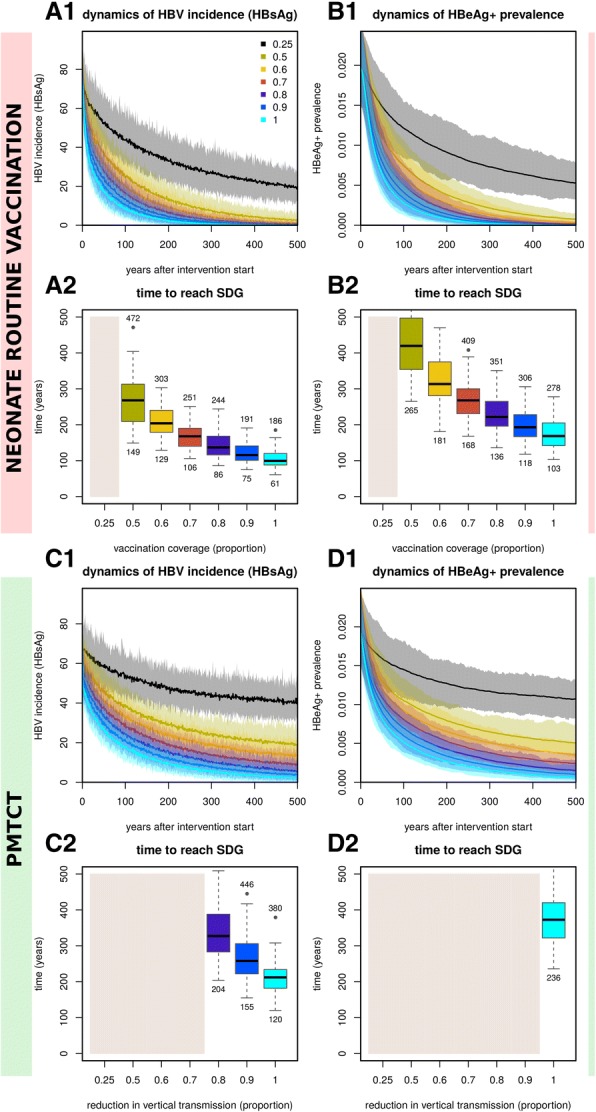
Stochastic impact of neonatal vaccination and PMTCT on HBV incidence (HBsAg) and HBeAg+ prevalence, showing time to reach Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) when using interventions independently. A1, A2 Impact on HBV incidence (HBsAg) (A1) and time to reach SDG (A2) for varying routine immunisation coverage of neonates. B1, B2 Impact on HBeAg+ prevalence (B1) and time to reach SDG (B2) for varying routine immunisation coverage of neonates. C1, C2 Impact on HBV incidence (HBsAg) (C1) and time to SDG (C2) for varying PMTCT coverage. D1, D2 Impact on HBeAg+ prevalence (D1) and time to reach elimination target (D2) for varying PMTCT coverage. A1, B1, C1, D1 Lines are the mean and shaded areas the standard deviation of model output when running 50 stochastic simulations per intervention (sampling the parameter posteriors shown in Fig. 1). A2, B2, C2, D2 HBV incidence (HBsAg) SDG is set to a reduction of 90%. HBeAg+ prevalence elimination target is set to 1/1000 individuals. Beige areas mark interventions reaching SDGs after 500 years on average. Boxplots show the variation of the 50 stochastic simulations. Numbers above and below boxplots show the 2.5% lower and 97.5% upper limits of the solutions. (All subplots) Intervention coverage varies from 0.25 to 1 (as coloured and named in subplot A1)
