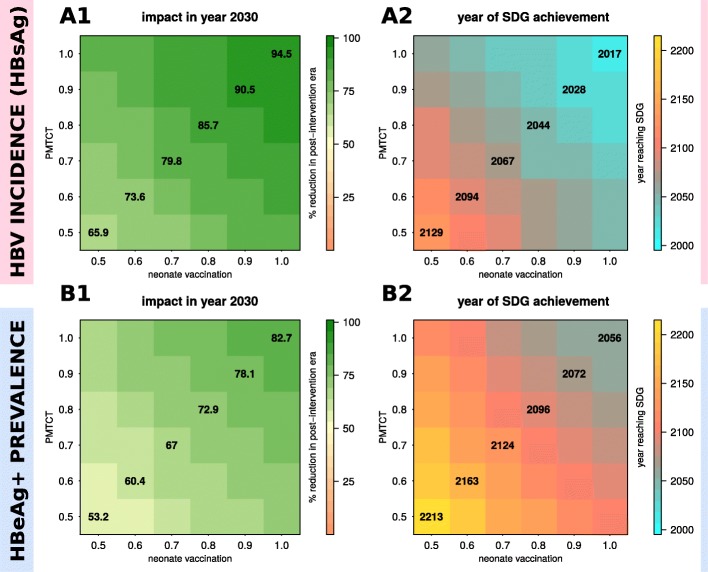
Fig. 5.
Sensitivity of mean intervention impact on HBV incidence (HBsAg) and HBeAg+ prevalence based on combinations of routine neonatal vaccination and PMTCT. A1, A2 Mean impact of interventions on HBV incidence (HBsAg) (A1) and mean time to reach Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (A2). B1, B2 Mean impact of interventions on HBeAg+ prevalence (B2) and mean time to reach elimination target (B2). For all subplots, impact is shown as percent reduction in incidence or prevalence compared to pre-intervention levels (e.g. 50 indicates a 50% reduction compared to before the start of the intervention). HBV incidence (HBsAg) SDG is set to a reduction of 90%. HBeAg+ prevalence target is set to 1/1000 individuals. Mean results are obtained from 50 stochastic simulations per intervention combination (vaccination, PMTCT) with parameters sampled from the posteriors shown in Additional file 2: Figure S1. Start of interventions in the stochastic simulations is in year 1995 to simulate an appropriate time scale to address impact by 2030