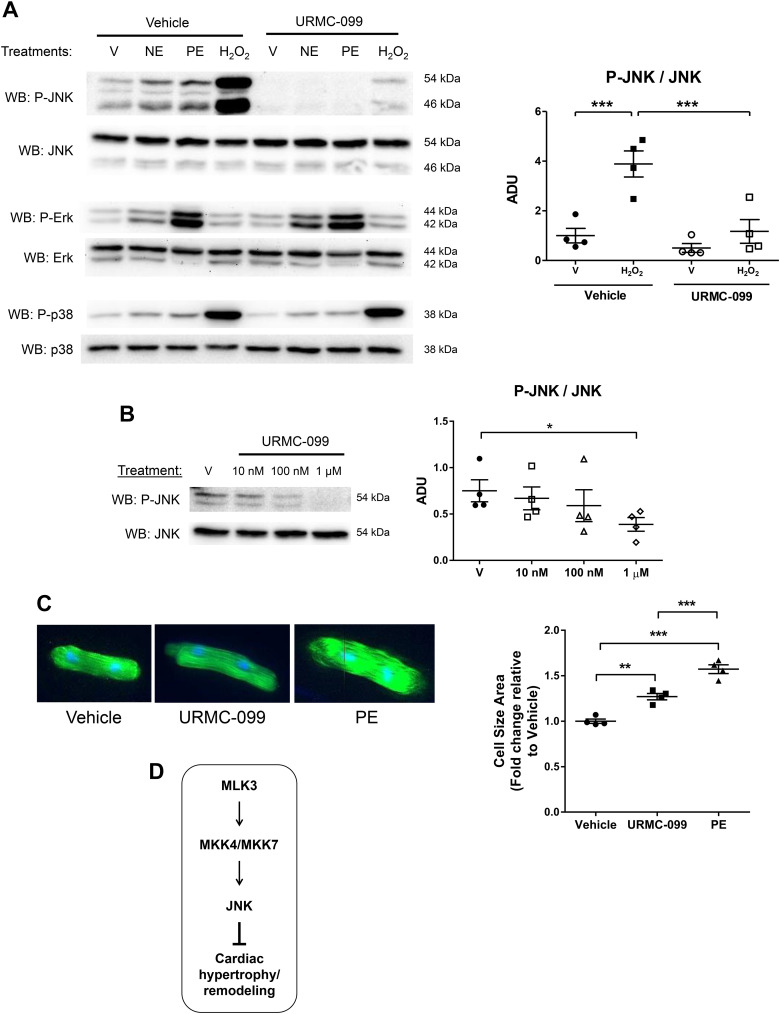
Fig. 7.
Administration of mixed lineage kinase-3 (MLK3) inhibitor selectively impairs c-Jun NH2 kinase (JNK) phosphorylation and promotes hypertrophy in cardiomyocytes. A: adult rat ventricular cardiomyocytes (ARVMs) were pretreated with vehicle (DMSO) or MLK3 kinase inhibitor URMC-099 (1 μM) for 60 min before stimulation with vehicle (H2O, labeled V), norepinephrine (NE, 1 μM, 20 min), phenylephrine (PE, 20 µM, 20 min), or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 100 µM, 60 min). Levels of phosphorylated (P-) and total forms of JNK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and p38 were evaluated by Western blotting. Representative blots are shown of n = 3–4 separate experiments. Densitometry of phosphorylated/total JNK is also shown. B: ARVMs were pretreated with DMSO vehicle (V) or URMC-099 (10 nM, 100 nM, or 1 μM) for 60 min. JNK phosphorylation was quantified and expressed relative to total JNK (n = 4, 54 kDa). C: ARVMs were treated with vehicle (DMSO), URMC-099 (100 nM), or DMSO + PE (20 μM) for 48 h. Cells were then fixed and stained with phalloidin and DAPI. Cardiomyocyte (CM) size was quantified and expressed as fold change relative to vehicle-treated cells (n = 4). For these experiments, each replicate represents an independent experiment from separate CM preparations; All data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s posttest. D: proposed model of antiremodeling MLK3-MAP kinase kinase-4 (MKK4)/MKK7-JNK signaling cascade in the CM.