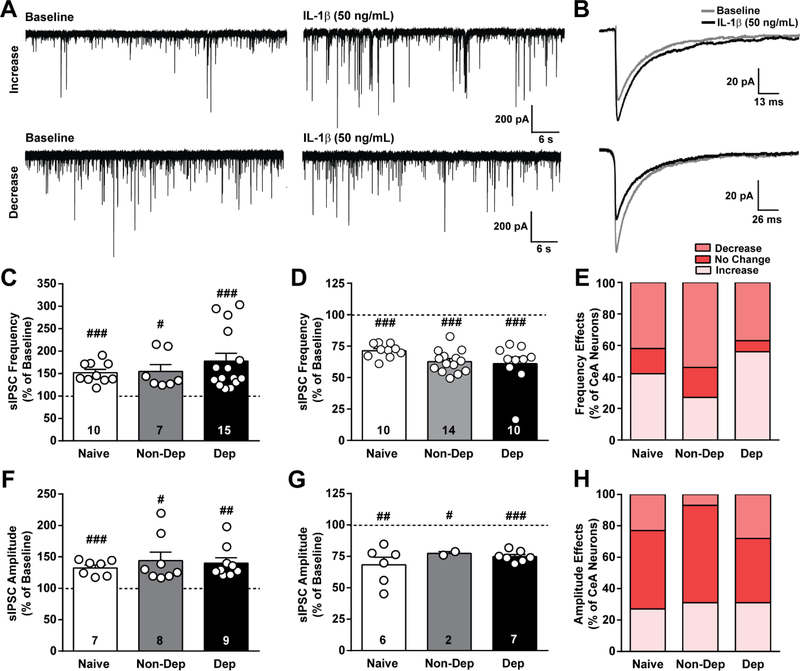
Figure 3. IL-1β effects on GABAergic transmission in the CeA of naïve, non-dependent, and dependent mice.
A. Representative traces of spontaneous action potential-dependent inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs) during baseline and during application of IL-1β (50 ng/mL) from CeA neurons of naïve mice showing an increase (top row) and decrease (bottom row) in sIPSCs induced by IL-1β. B. Average sIPSC from a single naïve cell showing either an increase (top) or decrease (bottom) in amplitude induced by IL-1β. C and D. IL-1β-induced increase and decrease, respectively, in sIPSC frequency plotted as a percent of baseline for naïve, Non-Dep, and Dep mice. E. Percent of CeA neurons responding to IL-1β with an increase, decrease or no change in sIPSC frequency. F and G. IL-1β-induced increase and decrease, respectively, in sIPSC amplitude plotted as a percent of baseline. H. Percent of CeA neurons reponding to IL-1β with an increase, decrease or no change in sIPSC amplitude. #, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001 by one-sample t-test; n = 24 – 27 cells from 14 – 15 mice per group, and the exact number of cells in each condition is reported in the bars.