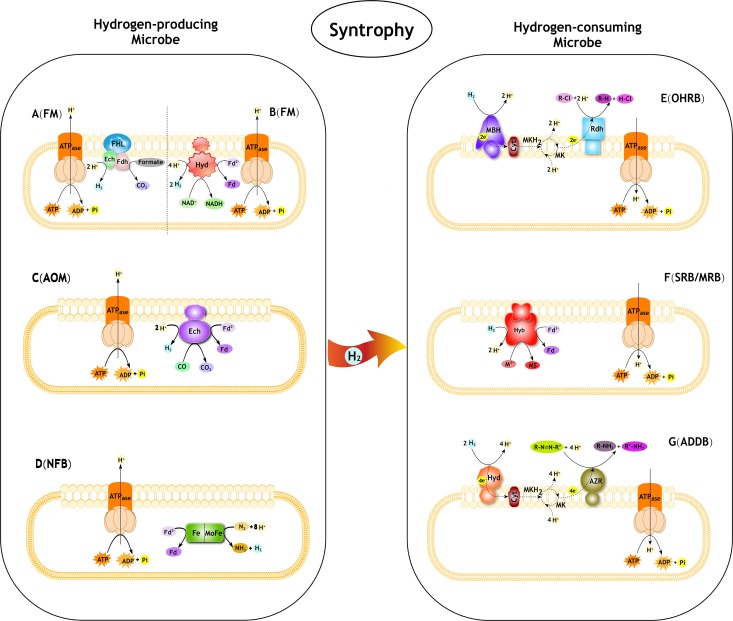
FIGURE 1.
Syntrophic interactions between hydrogen-producing and hydrogen-consuming microbes in pollutant degradation. FM, Fermentative microbe; AOM, Anaerobic CO oxidation microbe; NFB, Nitrogen-fixing bacteria; OHRB, Organohalide-respiring bacteria; SRB, Sulfate-reducing bacteria; MRB, Metal-reducing bacteria; ADDB, Azo dyes decolorization bacteria. (A) The progress of formate oxidation coupled to H2 formation in E. coli (derived from Sawers, 1994; Hallenbeck, 2009; Trchounian et al., 2012). The FHL complex consist of a Ech type membrane-bound H2-evolving [NiFe] hydrogenase coupled to a formate dehydrogenase (Fdh) and membrane integral subunits. (B) The progress of re-oxidation of NADH coupled to H2 formation in T. roseopersicina (derived from Jenney and Adams, 2008; Maróti et al., 2010). The Hyd is a membrane-bound H2-evolving [FeFe] hydrogenase. Fd, ferredoxin. (C) The progress of anaerobic CO oxidation coupled to H2 formation in C. hydrogenoformans (derived from Svetlichny et al., 1991; Soboh et al., 2002). The Ech is a membrane-bound H2-evolving [NiFe] hydrogenase. Fd, ferredoxin. (D) The progress of producing H2 as a byproduct of N2 fixation. The nitrogenase complex consist of a Fe protein and MoFe protein. (E) The role of H2 in reductive dechlorination in Dehalococcoides spp. (derived from Jugder et al., 2016). MBH, membrane-bound uptake hydrogenase. Cyt, cytochrome. MK, menaquinone; MKH2, dihydromenaquinone. Rdh, reductive dehalogenase. R-Cl, organohalide. (F) The role of H2 in reductive PTEs in Desulfovibrio fructosovorans (derived from Chardin et al., 2003; Cao et al., 2014). Hyb is a membrane-bound H2-uptake [NiFe] hydrogenase. Fd, ferredoxin. M, PTEs. MS, metal sulfides. (G) The role of H2 in reductive azo compounds in Shewanella decolorationis (derived from Hong et al., 2007, 2008). Hya, membrane-bound uptake [NiFe]-hydrogenase. Cyt, cytochrome. MK, menaquinone; MKH2, dihydromenaquinone. AZR, azo reductase.R-N = N-R’, azo compounds.