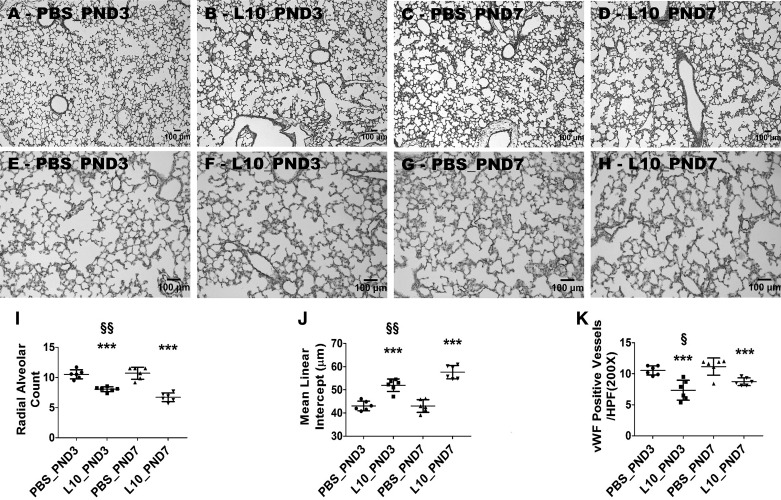
Fig. 10.
Deficits in development of saccular and alveolar lungs exposed to a single dose of LPS. Newborn mice were injected intraperitoneally with a single dose of vehicle control (PBS) or 10 mg/kg LPS (L10) on postnatal day (PND3) or PND7, and the lung tissues were harvested on PND14 for lung morphometry. Representative hematoxylin-eosin-stained lung sections obtained from mice treated on PND3 with PBS (A) and L10 (B) and on PND7 with PBS (C) and L10 (D). Representative von Willebrand factor (vWF)-immunostained lung sections obtained from mice treated on PND3 with PBS (E) and L10 (F) and on PND7 with PBS (G) and L10 (H). Alveolarization was quantified by determining radial alveolar counts (I) and mean linear intercepts (J), and pulmonary vascularization was quantified by counting the vWF-stained lung blood vessels (K). Values are presented as means ± SD (n = 6/group). Significant differences between age-matched PBS- and L10-exposed animals are indicated by ***P < 0.001. Significant differences between L10_PND3- and L10_PND7-exposed animals are indicated by §§P < 0.01 and §P < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA). Scale bar = 100 µM. L10_PND3, treated on PND3 with 10 mg/kg LPS; L10_PND7, treated on PND7 with 10 mg/kg LPS; PBS_PND3, treated on PND3 with PBS; PBS_PND7, treated on PND7 with PBS.