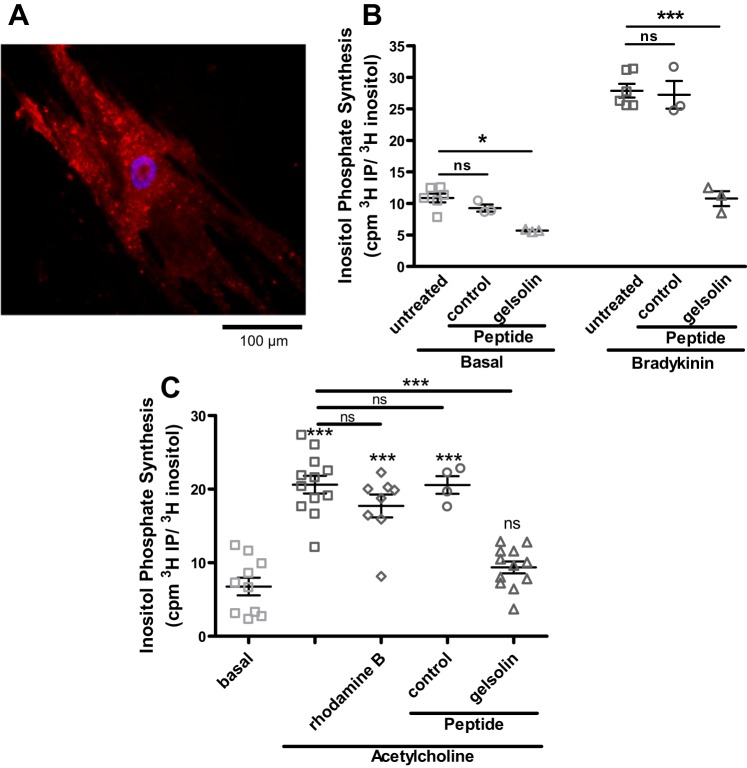
Fig. 1.
Gelsolin peptide introduction into primary cultures of human airway smooth muscle (ASM) cells and inositol triphosphate (IP3) synthesis decreases in response to the Gq-coupled agonists bradykinin and acetylcholine. A: representative fluorescent micrograph of primary human ASM cell after 1 h incubation with rhodamine B-conjugated gelsolin peptide. Scale bar = 100 µm. B: IP3 synthesis at 20 min in response to bradykinin in primary cultures of human ASM cells. Gelsolin peptide-treated cells generated less IP3 under basal and bradykinin conditions compared with untreated or control peptide treated cells (n = 3–6). C: IP3 synthesis in response to another Gq-coupled agonist acetylcholine in human ASM cells stably expressing the M3 muscarinic receptor. Gelsolin peptide-treated cells again generated less IP3 compared with controls (n = 4–12 from 3 different sets of experiments). cpm, Counts/min; ns, not significant. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ANOVA with Bonferroni comparison.