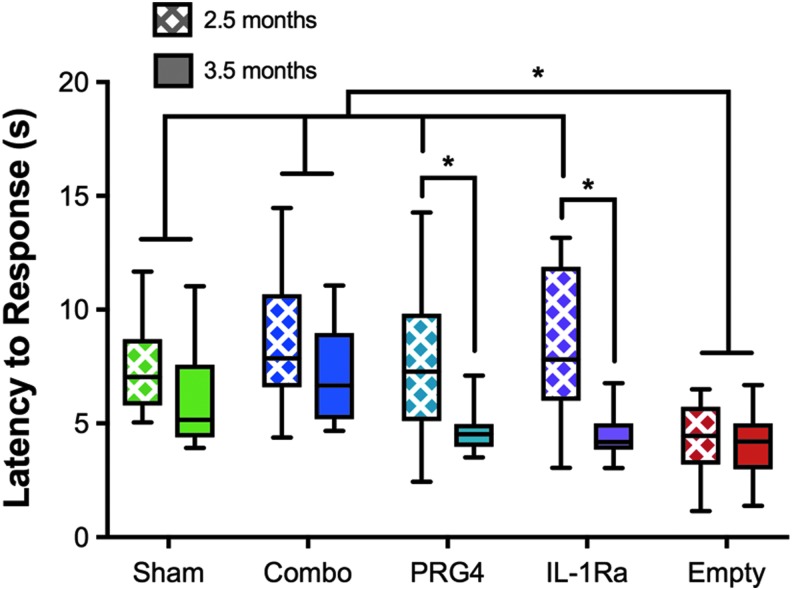
Figure 5.
Combinatorial therapy protects test animals from developing hyperalgesia in the mild-to-moderate posttraumatic OA model at both early and late time points. Behavior tests were conducted one week prior to collection. The untreated group responded significantly faster than sham controls at both early and late time points. Both monotherapy groups responded to the noxious thermal stimuli similarly to sham controls at 2.5 months after surgery; however, they develop a hyperalgesic response like the untreated animals at 3.5-months. Combinatorial therapy-treated animals responded like sham controls at both early and late time points, indicating a protection from the development of hyperalgesia. Data are represented by min-to-max box and whisker plots. N = 11 (2.5 months; Empty, 3.5 months; Sham) N = 12 (2.5 months; IL-1Ra), n = 13 (all other groups). *p < 0.05 ANOVA.