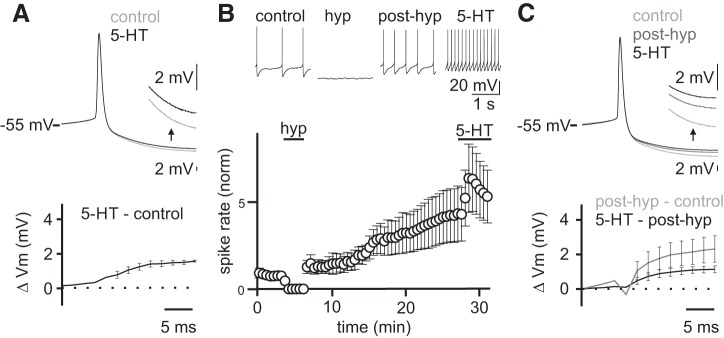
Fig. 3.
5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)-mediated increase in Golgi cell excitability is not occluded by hyperpolarization-induced firing rate potentiation. ΔVm, change in membrane potential. A: averaged Golgi cell action potential (AP) waveforms in control and following 5-HT application in the subset of cells with stable AP height (n = 3 cells). Inset shows expanded view of the afterhyperpolarization (AHP) (top). Subtraction between conditions (bottom). NBQX (5 μM), R-CPP (5 μM), and SR95531 (5 μM) included in all recordings. B: example Golgi cell recording showing APs from an experiment where a hyperpolarizing step (−50 pA, 3 min) was applied to induce firing rate potentiation before 5-HT application (top). Mean normalized firing rate across experiments (n = 5) (bottom). Error bars are means ± SE. C: averaged AP waveforms (n = 4) for each condition (top). Inset shows expanded view of the AHP. Subtractions of AP waveforms between subsequent conditions (bottom).