Fig. 5.
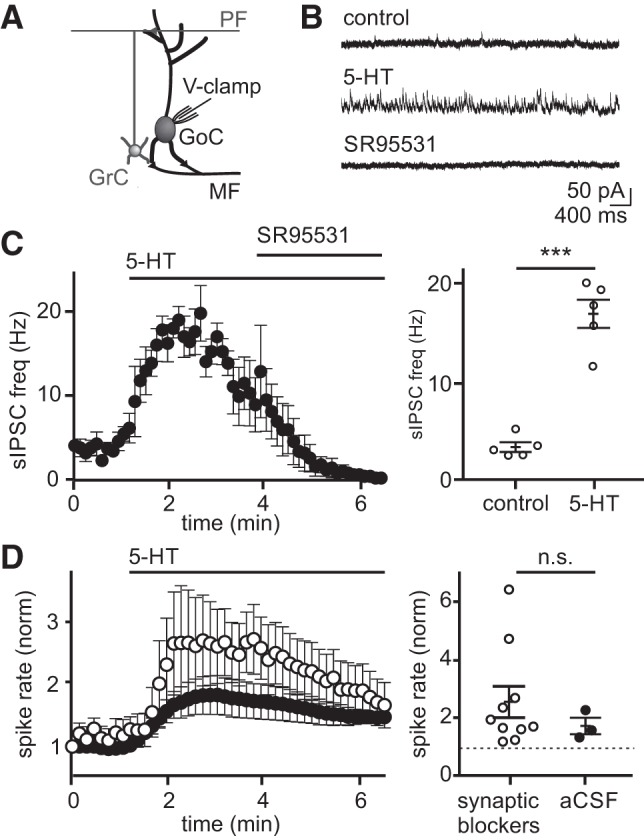
5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) increases the frequency of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs) on Golgi cells, reducing the magnitude of 5-HT-induced spike rate enhancement. A: schematic of the recording configuration. B: example Golgi cell voltage-clamp recording (0 mV) of sIPSCs before and after 5-HT application. C: mean sIPSC frequency before and during application of 5-HT (10 μM; n = 5) (left). Mean sIPSC rates measured at baseline and peak response for individual Golgi cells (right). Solid lines reflect mean and SE across the population. D: mean whole cell, current-clamp Golgi cell spike rate with (open circles, n = 10) and without (black circles, n = 3) synaptic transmission blockers [R-CPP (5 μM), NBQX (5 μM), SR95531 (5 μM)] (left). Mean spike rates measured at baseline and peak response for individual Golgi cells (right). Solid lines reflect mean and SE across the population. n.s., statistically nonsignificant; aCSF, artificial cerebrospinal fluid; ***P < 0.001.
