Fig. 2.
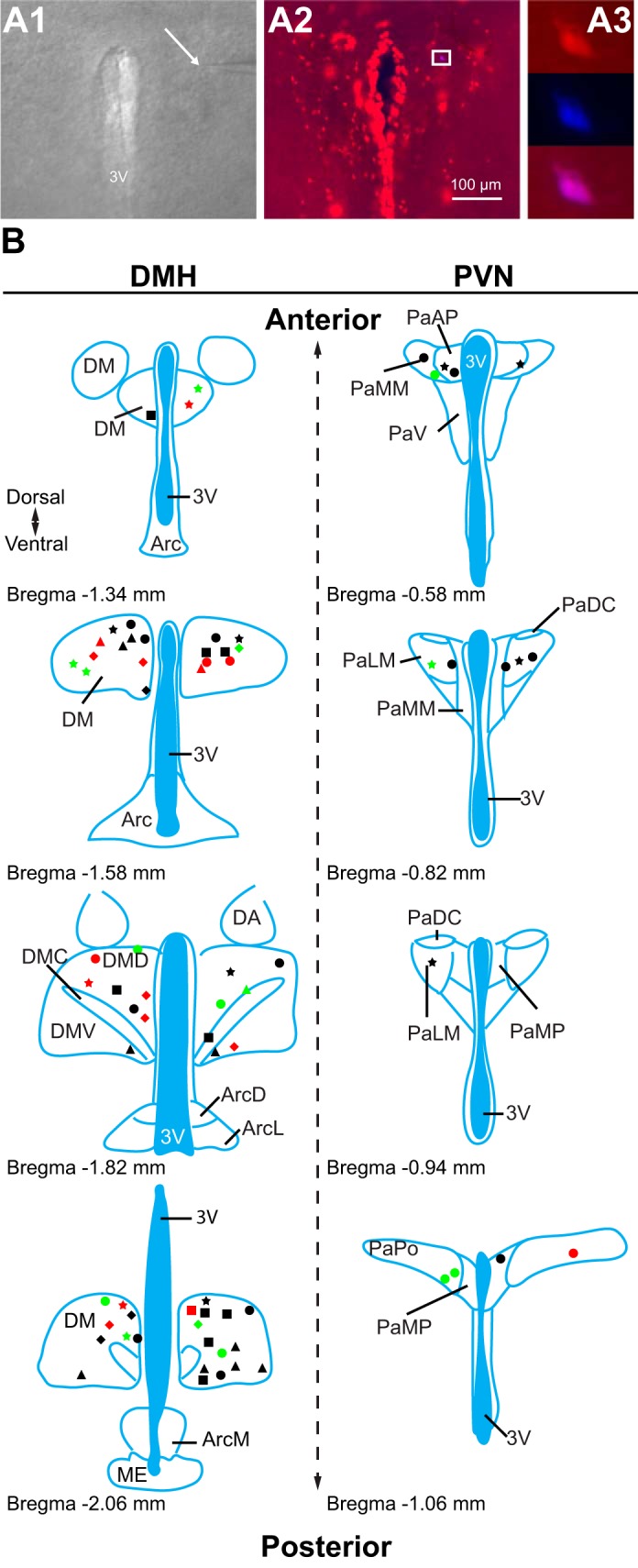
Location of recorded transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1)-expressing neurons. A: patch-clamp recordings were conducted from TRPV1-expressing neurons. A1: differential interference contrast image during patch-clamp recording (×4). Arrow points to the tip of a recording pipette. A2: TRPV1-expressing neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN; red, ×10). A3: enlarged view of boxed area shown in A2 (×40) illustrates a recorded TRPV1-expressing neuron (red) filled with Neurobiotin 350 (blue). B: schematic illustrations of the recorded TRPV1Cre/tdTom neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus (DMH) and the PVN. Each shape represents a different experimental setting as follows. In male mice: circle, miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) + capsaicin (Cap); square, mEPSCs +5′-iodoresiniferatoxin (5′-IRTX) + Cap; triangle, mEPSC + fluorocitrate (FC) + Cap; star, mIPSCs + Cap; in female mice: diamond, mEPSCs + Cap. Red indicates the location of neurons that had increased frequency after Cap application, green indicates the location of neurons that had decreased frequency, and black indicates the location of neurons not responding to Cap. 3V, 3rd ventricle; DM, DMH; DMD, dorsal part of DMH; DMC, compact part of DMH; DMV, ventral part of DMH; Arc, arcuate nucleus; ArcD, dorsal part of Arc; ArcL, lateral part of Arc; ArcM, medial part of Arc; ME, median eminence; DA, dorsal hypothalamic area; Pa, PVN; PaAP, anterior PVN; PaMM, medial magnocellular PVN; PaV, ventral PVN; PaDC, dorsal cap of PVN; PaLM, lateral PVN; PaMP, medial PVN; PaPO, posterior PVN. Schematics are based on Franklin and Paxinos (2007).
