Figure 4.
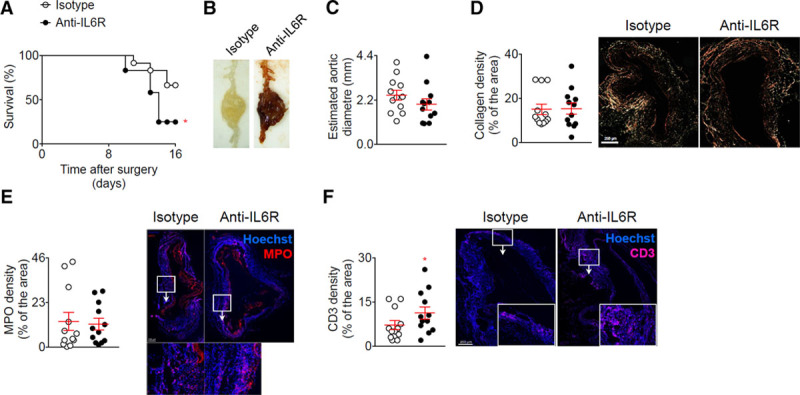
Blockage of the IL (interleukin)-6 pathway using anti-IL-6R in the elastase + anti-TGF (transforming growth factor)-β model enhances T-cell infiltration and rupture of the aorta. Mice were treated with anti-IL-6R or isotype control (n=12 mice/group) starting one week before the application of elastase and the infusion anti-TGF-β. A, Survival curves of mice after the application of elastase and the infusion anti-TGF-β. *P<0.05 isotype vs anti-IL-6R; Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test. B, Representative macroscopic pictures of abdominal aortic aneurysms from mice treated with elastase and anti-TGF-β and isotope or anti-IL-6R, at day 16. Note that the aneurysm from the isotype treated mouse was not ruptured. C, Analysis of the aortic diameter (µm) based on the perimeter obtained from aortic cross sections. D, Quantification and representative images of collagen content of the aortic wall analyzed using Sirius Red staining under polarized light. E and F, Quantification and representative images of myeloperoxidase (MPO) (D) and CD3 (E) immunofluorescent stainings on aortic cross section. *P<0.05 isotype vs anti-IL-6R; Mann-Whitney test. All data for the generation of the graphs shown in Figure 4 were generated in one independent experiment.
