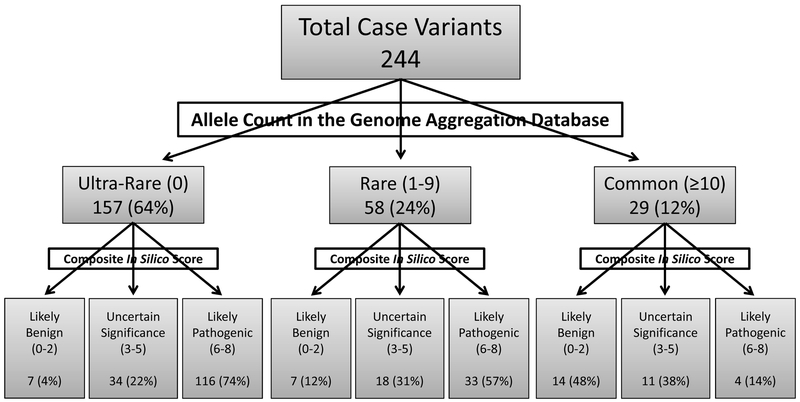
Figure 1. Breakdown of KCNQ1 case-derived missense variants in gnomAD and after in silico pathogenicity analysis.
Each of 244 unique KCNQ1 case-derived MVs were assessed for rarity using gnomAD. Variants were considered “ultra-rare” if completely absent (allele count = 0), “rare” if seen 1 to 9 times, or “common” if seen in ≥10 individuals within gnomAD. In silico analysis was conducted using eight publically available tools to assess the predicted pathogenicity of all KCNQ1 case-derived MVs. Each variant was placed into one of three categories based on how many tools predicted that variant to be pathogenic: likely benign (≤ 2 tools), uncertain significance (3-5 tools), or likely pathogenic (≥ 6 tools).