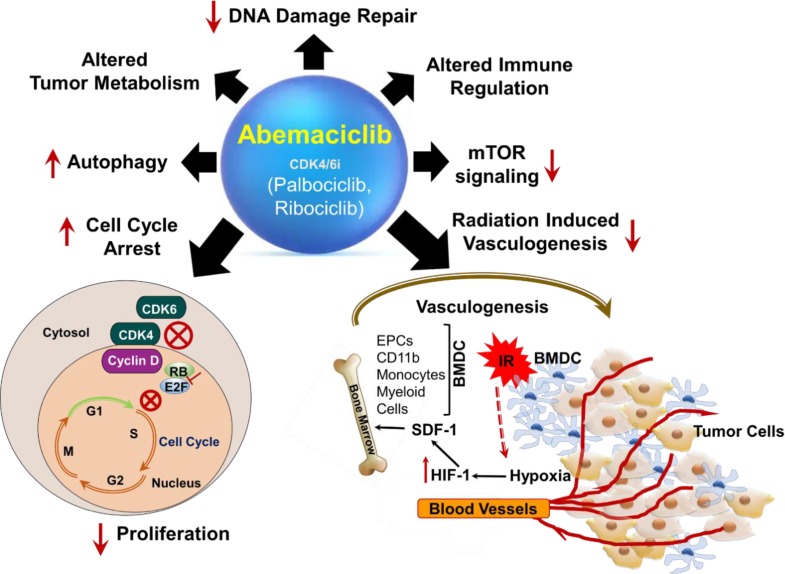
Figure 1. Abemaciclib, a selective CDK4/6 inhibitor with multiple actions.
CDK4/6 inhibitors (Abemaciclib, Palbociclib and Ribociclib) are cell cycle blockers mainly at the G1/S border. In the presence of these inhibitors, CDK4/6-cyclinD complex formation is inhibited resulting in reduced phosphorylation of RB (Retinoblastoma) protein and release of E2F transcription factor inside the nucleus to drive cells in the replicative (S) phase of cell cycle. Some numerous potential targets within the tumor microenvironment (TME) whose modulation may lead to radiosensitisation on tumor cells by Abemaciclib is highlighted and described in the text. Prior to irradiation, tumor growth is governed largely by local angiogenesis. When local angiogenesis is inhibited by irradiation, growth of the tumor vasculature (essential for recurrence of the tumor) can occur from circulating cells, of which BMDCs (Bone Marrow Derived Cells) such as CD11b+ monocytes, myeloid cells and EPCs (Endothelial Progenitors Cells) are an essential component. After irradiation, the tumor becomes more hypoxic, and HIF-1 (Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1) is increased as the tumor attempts to regrow. This induces SDF-1 (Stroma Derived Factor-1) and promotes the mobilization of CD11b+ monocytes from the BM (Bone Marrow) and retention of these BMDCs into the tumor. SDF-1 is the key factor for the influx of BMDC. Abemaciclib, inhibits restoration of tumor vasculature post radiotherapy by inhibiting HIF-1 and SDF-1 expression in the tumor microenvironment.