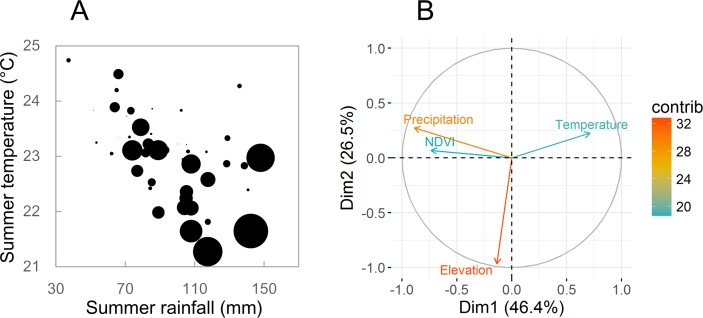
Fig 3. Environmental factors associated with hantavirus disease outbreaks.
(A) Relationship between summer temperature, summer rainfall, and HFRS cases in Weihe Plain, North China, 1960 to 2013. Circle size is proportionate to the number of HFRS cases [46]. (B) Contribution of the environmental variables to the explained variance of hantavirus-antibody–positive in rodents using a multivariate principal component analysis in Hunan Province, South China, 2007 to 2010. Dimensions 1 and 2 are the spaces where variables are expressed. The length (angle) of the arrows represents the magnitude (direction) of the correlation coefficient between the variable and the principal components. The contributions of the variables to the hantavirus-antibody–positive in rodents are ranked with colors ranging from green to red, respectively (reproduced from Xiao 2016 with permission of the publisher [127]). Dim, dimension; HFRS, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome; NDVI, normalized difference vegetation index.