Fig 2. hCCS dimer interface destabilisation.
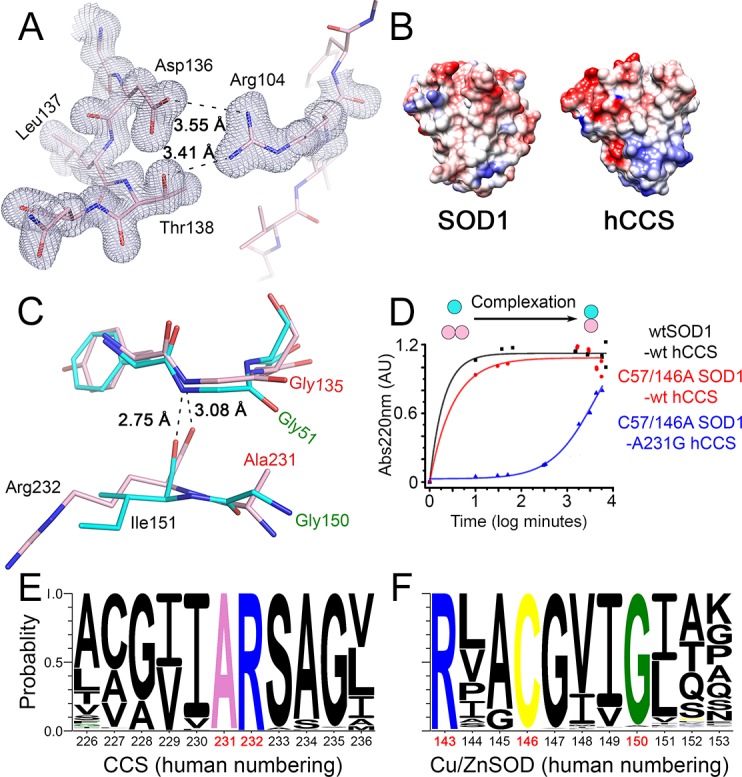
(A) Electron density map (2Fo-Fc, contoured at 1σ level) showing the Coulombic interaction between hCCS Arg104 and Asp136/Thr138. (B) Surface charge maps of hSOD1 and hCCS domain II dimer interface surfaces. (C) The hCCS (pink) dimer interface Arg232-Gly135 hydrogen bond is weakened by the steric effect of Ala231 side chain. The hCCS Gly135-Asp136 carbonyl rotates to accommodate the methyl group, and Gly135 is pushed away from Arg232. hSOD1 (cyan) Gly150 maximises hydrogen bond strength between Phe51 and Ile151. (D) Restoring SOD1-like dimer affinity with the Ala231Gly hCCS mutation vastly slows complexation. (E) Eukaryotic CCS sequence diversity shows Ala231 is very highly conserved despite its detrimental effect on homodimer affinity. (F) SOD1 Gly150 is equally well conserved, indicating the relative balance of SOD1 and CCS homodimer affinities is evolutionarily static. AU, absorbance unit; CCS, copper chaperone for SOD1; hCCS, human copper chaperone for SOD1; hSOD1, human superoxide dismutase-1; SOD1, superoxide dismutase-1; wt, wild-type.
