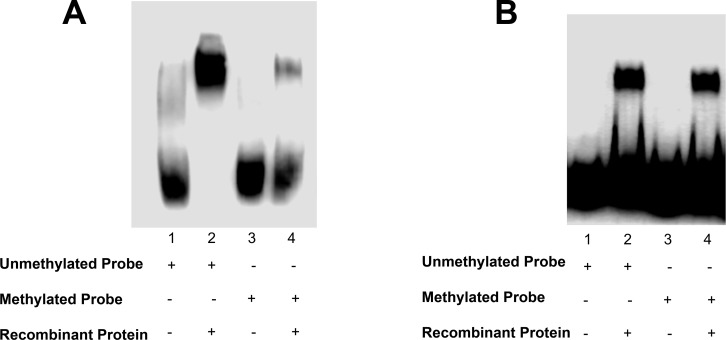
Fig 10. The effect of methylation on Elk1 binding.
(A) Unmethylated biotin-labeled WT oligonucleotide including +113/+122 Elk1 binding site on KATNA1 is shown in lane 1. When +113/+122 Elk1 binding site is incubated with Elk1-db protein, shift band is observed (lane 2). This oligonucleotide was methylated and loaded as control (lane 3). In the presence of Elk1-db protein and methylated oligonucleotide, the shift band intensity (lane 4) is clearly lower compared to unmethylated oligo (lane 2) (n = 3). (B) Elk1 binding is observed when incubated with unmethylated SPG4 oligonucleotide including -235/-226 binding site (lane 2). Also, methylated form of this oligonucleotide could not prevent the complex formation with Elk-1 (lane 4). Both unmethylated and methylated probes were separately loaded as controls (lane 1 and 3, respectively) (n = 3).