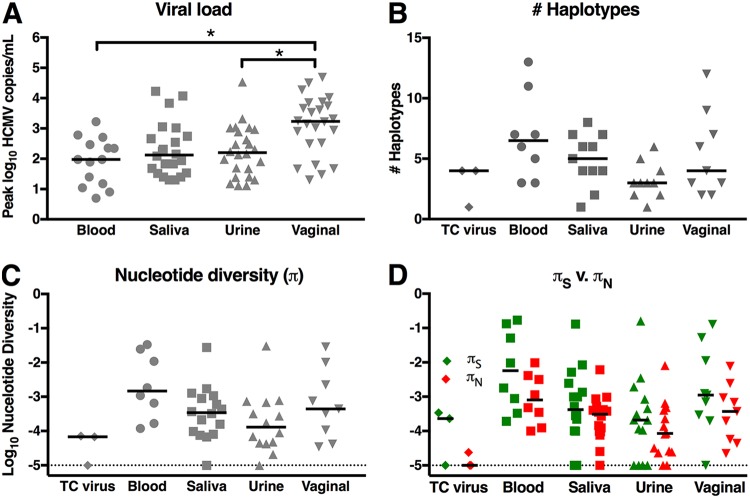
FIG 2.
High-magnitude viral shedding in vaginal fluid, yet similar numbers of unique viral variants and nucleotide diversity between anatomic compartments. Peak viral loads were compared between anatomic compartments for 11 gB/MF59 vaccinees, 22 placebo recipients, and 4 seropositive individuals (A), revealing high-magnitude HCMV shedding in vaginal fluid. Using SNAPP NGS data, the peak numbers of unique viral haplotypes (B) and peak nucleotide diversity (π) (C) were defined according to individuals for each anatomic compartment, resulting in data from 8 whole blood, 11 saliva, 10 urine, and 9 vaginal fluid samples from acutely infected gB vaccinees and placebo recipients as well as chronically HCMV-infected individuals. (G) The magnitudes of nucleotide diversity resulting in synonymous (πS) versus nonsynonymous changes (πN) were compared. Horizontal bars indicate the median values for each group. *, P < 0.05 according to statistical tests: viral load, Friedman test plus post hoc pairwise Wilcoxon signed-rank test; haplotypes and π, Kruskal-Wallis test plus post hoc exact Wilcoxon rank sum test; πS versus πN, Wilcoxon signed-rank test.