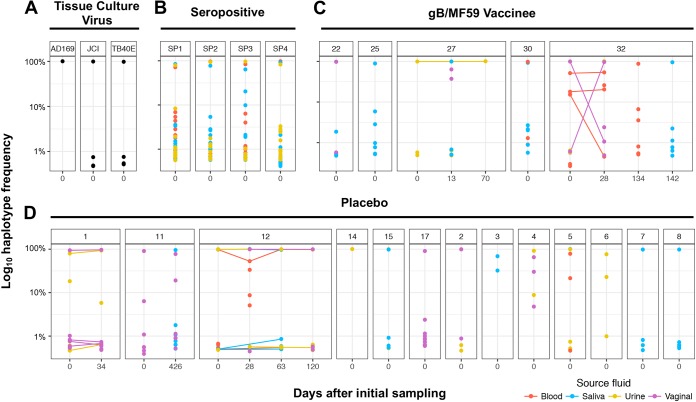
FIG 3.
Large numbers of low-frequency viral variants detected at gB locus in both primary HCMV-infected and chronically infected individuals. The relative frequency of each unique gB haplotype identified by SNAPP is displayed by individual patient and time point of sample collection. Tissue culture viruses (A) exhibited reduced population complexity by comparison. In primary HCMV-infected placebo recipients (C) and gB vaccinees (D), as well as chronically HCMV-infected women (B), there were typically one or more high-frequency haplotypes representing the dominant viral variants within the population, which were accompanied by haplotypes at very low frequency representing minor viral variants (<1% of viral haplotype prevalence). All haplotypes displayed exceeded the 0.44% threshold of PCR and sequencing error established for the SNAPP method (see Materials and Methods for detail).