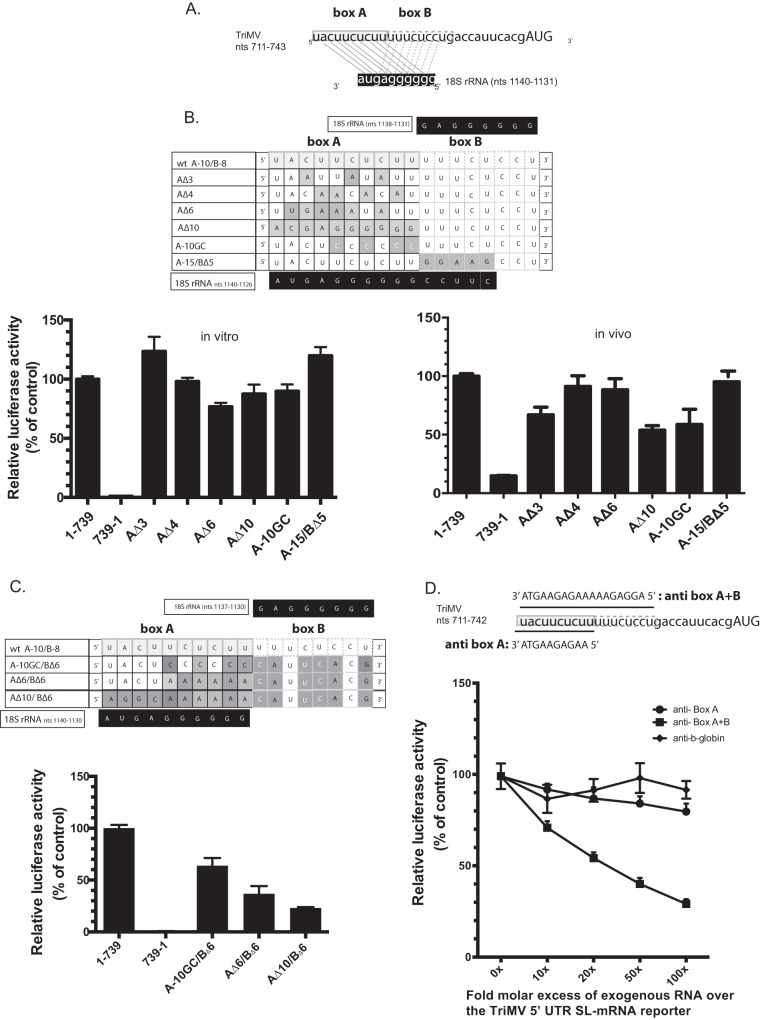
FIG 3.
The TriMV YX-AUG motif likely functions as target sites for the 18S rRNA binding (A) Sequence showing the two adjacent putative binding sites (box A and box B) of the TriMV IRES at positions nt 711 to 720 and nt 721 to 728 to a highly conserved region of the 18S rRNA at positions nt 1123 to 1140. (B) The mutated bases within the TriMV box A 18S rRNA target site that either partially or fully decreased (AΔ3, AΔ4, AΔ6, and AΔ10), increased (A-15/BΔ5) base pairing interaction or strengthened (A10-GC with the wobble base pairs within box A replaced with GC pairs) are shaded. The wild-type sequence is annotated as “wt A-10/B-8”. The relative luciferase activity in wheat germ extract (on the left) and in oat protoplasts (on the right) of the different TriMV mutants is relativized to that of the TriMV wild-type sequence. For the oat protoplast assays, the reporter mRNAs were coelectroporated with a m7GpppG capped polyadenylated renilla mRNA used as an internal control at a 1:10 ratio. (C) The mutated bases within the TriMV box A and box B 18S rRNA target sites that reduced the overall base pairing interaction and the CU-richness of the region are shaded. The wild-type sequence is annotated as “wt A-10/B-8”. The relative luciferase activity of the TriMV 5′ UTR with different mutations across the box A and box B 18S rRNA binding sites in wheat germ extract is relativized to that of the wild-type sequence in the presence of the strong hairpin. (D). trans-Inhibition assay of the TriMV 5′ UTR SL-mRNA with increasing molecular excess of antisense single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides targeting the box A (anti-BoxA) or both box A and box B (anti-BoxB) 18S rRNA binding sites in wheat germ extract. As a control DNA oligonucleotides targeting unrelated human β-globin sequence was added. A 0- to 100-fold molar excess of the antisense oligonucleotides was added to the reaction.