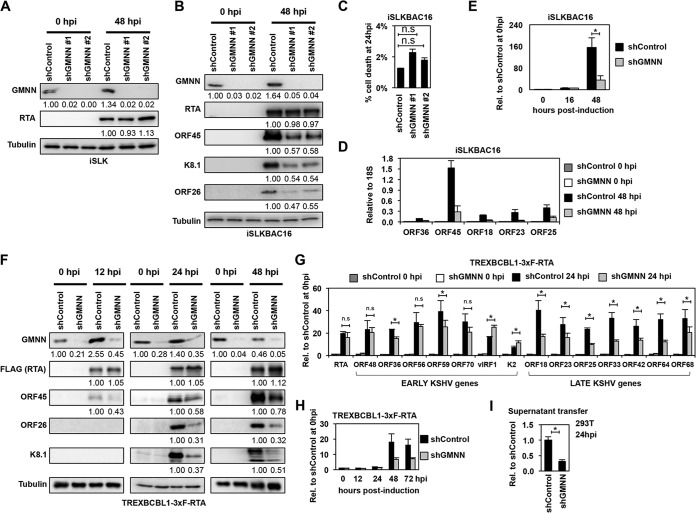
FIG 8.
Effect of geminin on KSHV lytic reactivation. (A and B) Immunoblot analysis of RTA and GMNN expression in shControl- and shGMNN-treated iSLK cells and the expression of KSHV proteins in shRNA-treated iSLKBAC16 cells at 0 hpi and 48 hpi. (C) Cell death analysis in shRNA-treated reactivated iSLKBAC16 cells at 24 hpi. (D) RT-qPCR analysis of viral gene expression in shControl- and shGMNN #1-treated iSLKBAC16 cells. (E) The copy number of KSHV genome in the shGMNN #1- and shControl-treated iSLKBAC16 cells was determined at the indicated time points of KSHV reactivation relative to 0 hpi. (F) Immunoblot analysis of the expression of viral proteins in shControl- and shGMNN-treated TRExBCBL1-3×FLAG-RTA cells at 0 hpi (latency), 12 hpi, 24 hpi, and 48 hpi. The quantification of protein expression on the immunoblots is shown as relative fold change. (G) Testing the expression of viral genes by RT-qPCR in shGMNN-treated TRExBCBL1-3×FLAG-RTA cells compared to shControl-treated cells at 0 hpi and 24 hpi. (H) The relative KSHV DNA load in shControl- and shGMNN-treated TRExBCBL1-3×FLAG-RTA cells at different time points of KSHV reactivation compared to 0 hpi (latency). (I) The same amount of supernatants from shControl and shGMNN samples at 72 hpi described in panel H was used to infect 293T cells, and the viral DNA level was measured in the infected cells by qPCR at 24 hpi. n.s., nonsignificant; *, P < 0.05.