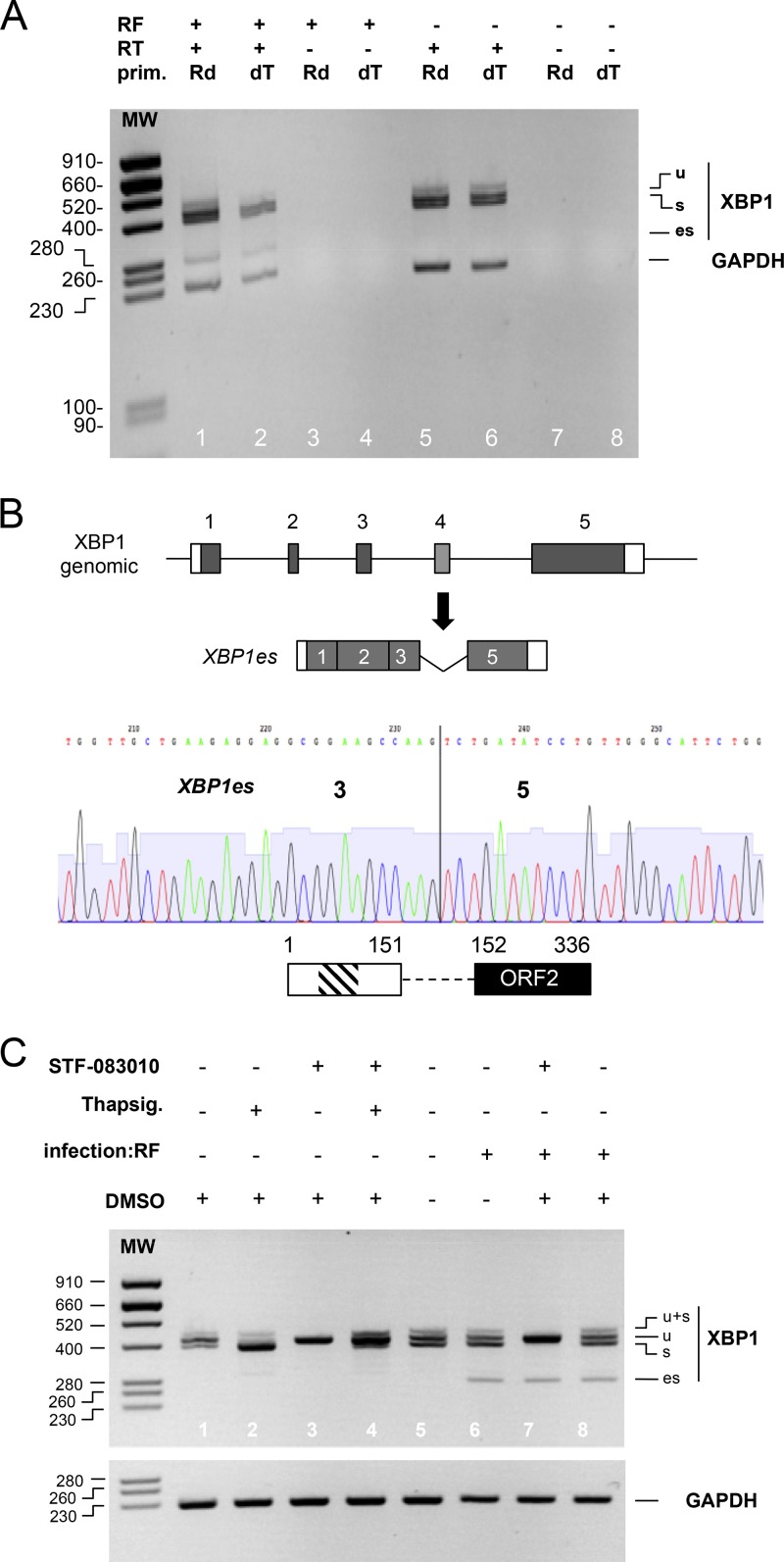
FIG 2.
XBP1es is a poly(A) RNA that results from exon skipping, not cytoplasmic splicing. (A) RNA purified from mock (RF–)- or rotavirus RF (RF+)-infected cells was used as the template for a reverse transcription reaction with (RT+) or without (RT–) reverse transcriptase and using oligo(dT) (dT) or random hexanucleotides (Rd) as primers. DNA products obtained by the PCRs using either XBPdir and XBPrev primers or GAPDH primers were analyzed by electrophoresis on the same agarose gel. The sizes of the molecular weight markers (MW) are indicated (in base pairs) on the left side. (B) A chromatogram from Sanger sequencing of the XBP1es RT-PCR DNA product is shown below a schematic representation of the organization of the XBP1 gene and that of XBP1es RNA resulting from exon 4 skipping. The vertical line marks the junction of the exon 3 and 5 sequences. A schematic representation of the putative translation product of XBP1es RNA is shown with the DNA-binding (hatched box) and transactivating domains (black box). The numbers indicate amino acid positions. (C) RNA purified from MA104 cells infected (for 9 h) or not by the RF strain of rotavirus and treated with the IRE1α inhibitor STF-083010 in DMSO (60 μM), with the IRE1α activator thapsigargin (400 nM) or with DMSO (used as vehicle for STF-083010), was subjected to RT-PCR with XBP1 primers and GAPDH primers. The PCR DNA products were analyzed by electrophoresis on two agarose gels. The sizes of the molecular weight markers (MW) are indicated (in base pairs) on the left.