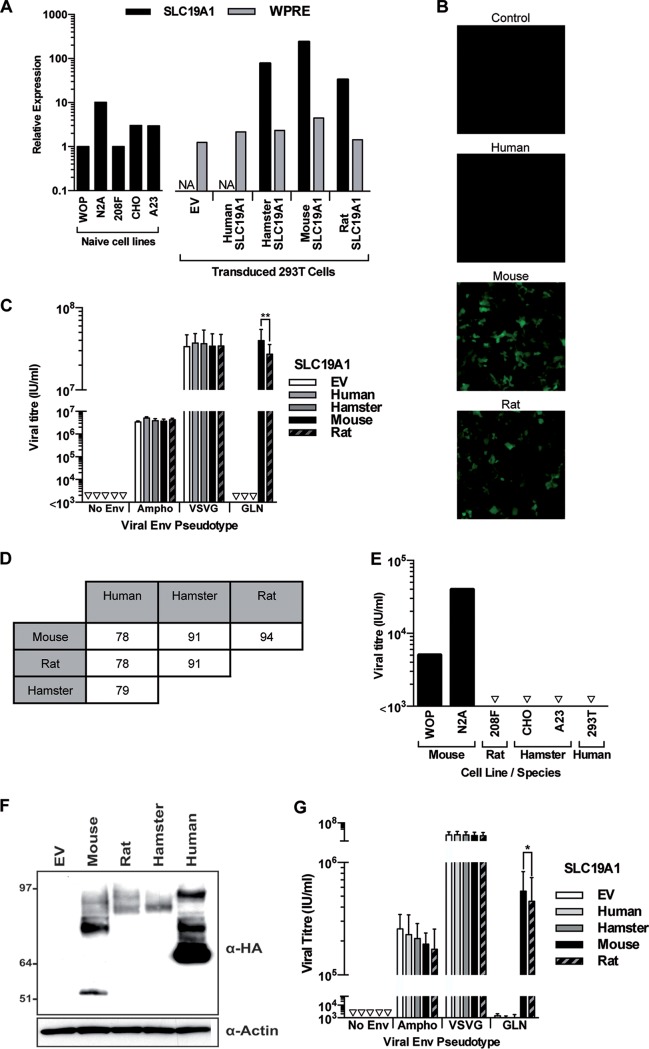
FIG 4.
Specificity of SLC19A1 as the cellular receptor for GLN. 293T cells were transduced to express SLC19A1 from different species before being exposed to GFP-expressing pseudotyped viruses. (A) RT-qPCR was used to measure the relative expression of SLC19A1 from different rodent cell lines and the exogenous expression of the SLC19A1 transgenes in stably transduced 293T cells. NA, not applicable, as the SLC19A1 qPCR oligonucleotides are able to detect only rodent versions of the transcript (100% homology with mouse, rat, and hamster sequences) and were not used to analyze empty vector- and human SLC19A1-transduced cells. Therefore, relative expression of the transgene was also assessed by detection of the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) (WPRE) present in all lentiviral constructs. Levels of both transcripts were normalized to the level of the housekeeping gene RPLPO. Expression levels of SLC19A1 and WPRE are shown relative to those in WOP and empty vector-transduced 293T cells, respectively. This measurement was performed once using one set of cells that were used for the experiment in panel B. Bars represent average values from 2 technical replicates. (B and C) Infection by GLN was assessed by fluorescence (B), and the titers of viruses pseudotyped with Ampho, VSV-G, GLN Envs, or a no-Env control were calculated by flow cytometry (C) (**, P < 0.01 by a paired t test; n = 3 except for GLN infections [n = 6]; the SD are represented by the error bars). (D) Amino acid similarity of the SLC19A1 sequences between different species. (E) Demonstration of the species tropism of GLN by infection of cell lines of different rodent species as well as of the human 293T cell line after transduction with mouse SLC19A1. Note that the differences in the titers observed between the mouse WOP and N2A cell lines is likely due to the difference in SLC19A1 expression levels (panel A), since we ensured by sequencing that both cell lines express identical versions of the SLC19A1 gene. Shown are data from one representative experiment out of three. (F) 293T cells were transduced with 3′ HA-tagged versions of the SLC19A1 genes. Western blotting was used to detect expression of the protein using an anti-HA antibody. The image shown is representative of results from 3 independent experiments. (G) 293T cells expressing the HA-tagged versions of the SLC19A1 constructs were exposed to GFP-expressing pseudotyped viruses. (*, P < 0.05 by a paired t test; n = 4).