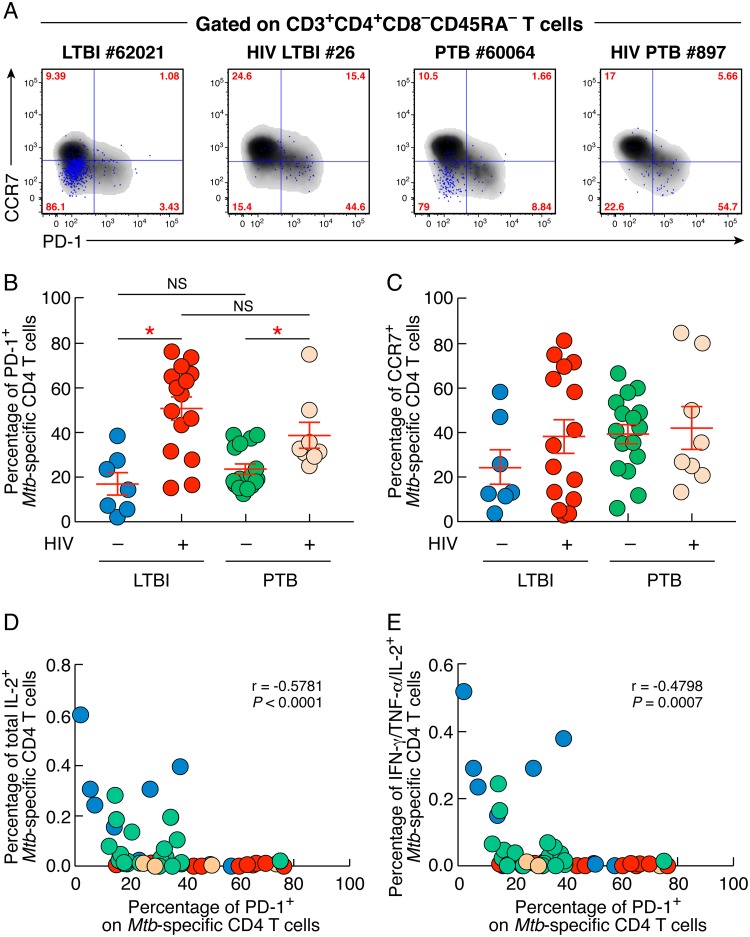
FIG 4.
HIV infection influences PD-1 expression on M. tuberculosis-specific CD4 T cells. (A) Representative flow cytometry profile of M. tuberculosis-specific memory (CD45RA−) CD4 T cells (blue dots) isolated from one individual with LTBI (62021), HIV/LTBI (26), PTB (60064), or HIV/PTB (897) expressing PD-1 and/or CCR7. (B and C) Percentages of M. tuberculosis-specific CD4 T cells isolated from individuals with LTBI (n = 7), HIV/LTBI (n = 15), PTB (n = 16), or HIV/PTB (n = 8) expressing PD-1 (B) and/or CCR7 (C). (D and E) Correlation between the percentage of M. tuberculosis-specific CD4 T cells expressing PD-1 and the percentage of total IL-2-producing M. tuberculosis-specific memory CD4 T cells (D) or the percentage of IFN-γ/IL-2/TNF-α-producing M. tuberculosis-specific memory CD4 T cells of individuals with LTBI (n = 7), HIV/LTBI (n = 15), PTB (n = 16) or HIV/PTB (n = 8) (E). Statistical significance (*; P < 0.05) was calculated using one-way ANOVA (Kruskal-Wallis test) followed by the Mann-Whitney test (B and C) or Spearman rank test for correlation (D and E).