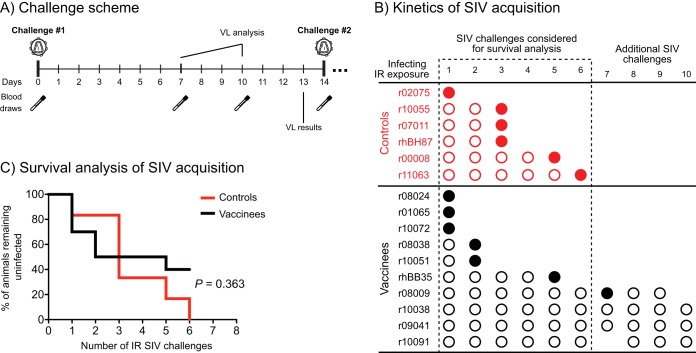
FIG 6.
Acquisition of SIV infection in vaccinees and control animals. (A) Challenge scheme. Macaques were exposed to SIV on day 0 and subsequently bled on days 7 and 10. Plasma collected on days 7 and 10 was assayed for the presence of SIV RNA, and a decision was made as to whether or not to challenge the animals on day 14. Macaques that remained aviremic on both days 7 and 10 were rechallenged, whereas monkeys with a positive VL on either of these days were not rechallenged. (B) Kinetics of SIVmac239 acquisition in vaccinated and control macaques. Individual animals in the vaccine and control groups are depicted along with the IR SIVmac239 exposures that caused (filled circles) or did not cause (empty circles) productive infection. Although macaque r08009 likely acquired infection after the 7th SIV exposure, it ended up being challenged 9 times (see the text for details). Macaque r10091 skipped challenge 7 but was rechallenged two additional times (see the text for details). (C) Survival analysis of SIV-infected vaccinated and control animals. The P value was determined by the Cox proportional hazard model (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.19 to 1.85).