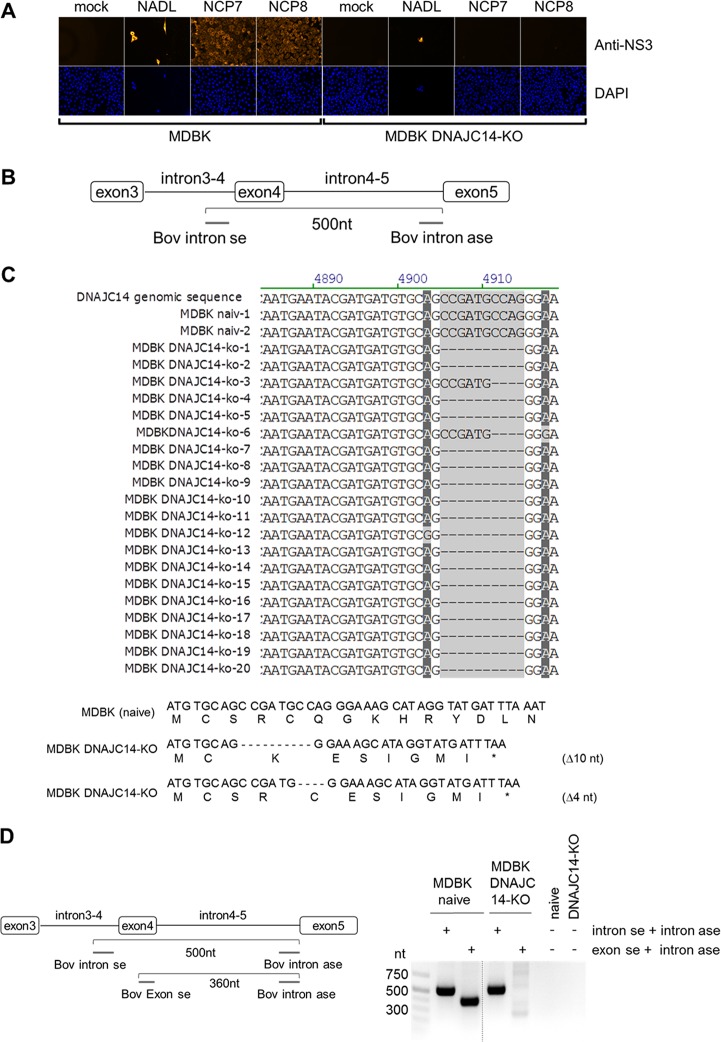
FIG 2.
Establishment and functional characterization of MDBK DNAJC14-KO cells. (A, upper) Naïve MDBK cells and MDBK DNAJC14-KO cell clones were infected with the indicated viruses (NCP7, NCP8, and NADL) at an MOI of 3 and analyzed by NS3-specific IF assay at 72 hpi. (Lower) Cell nuclei were visualized by DAPI staining. (B) Scheme of the genomic PCR amplification depicting the relative positions of the intron-specific primer flanking exon 4 of the bovine DNAJC14 genomic DNA. (C, upper) Analysis of PCR amplicons obtained from PCR amplification of genomic DNA isolated from naive MDBK cells (2 amplicons, naive 1 and 2) and MDBK DNAJC14-KO cell clone 2 (20 amplicons, MDBK DNAJC14-KO amplicons 1 to 20). Sequences surrounding the DNAJC14-specific guide RNA-mediated genome alteration are shown. Bovine DNAJC14 genomic DNA sequence is shown at the top as a reference. (Lower) Bovine DNAJC14 DNA sequence and amino acid sequence are depicted for naive MDBK cells (top) and MDBK DNAJC14-KO cell clone 2 with the two identified guide RNA-mediated DNAJC14 genome alterations (Δ10 and Δ4). The depicted amino acid sequence starts with the beginning of the Jiv90 domain. Positions of the stop codons resulting from deletions introduced by the DNAJC14 guide RNA are indicated by a star. (D) Seminested PCR analysis to confirm MDBK DNAJC14-KO phenotype. (Left) Scheme of the seminested PCR assay depicting the position of intron- and exon-specific primers on the DNAJC14 genomic DNA. The gel-purified intron-specific amplicons (approximately 500 nt) were used as the template for seminested PCR using DNAJC14 exon- and intron-specific primers (product size, 360 nt) to further verify KO cell clones. (Right) Agarose gel analysis of seminested PCR products. The size standard is given on the left.