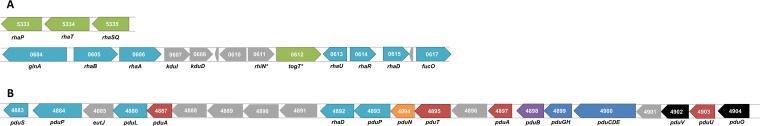
FIG 2.
Schemes of the rhamnose utilization (A) and bacterial microcompartment (BMC) (B) clusters in C. beijerinckii DSM 6423. (A) The genes predicted to encode enzymes involved in the L-rhamnose metabolism are shown in blue, the genes in green encode putative l-rhamnose transporters, and the genes in gray are not reported to be involved in l-rhamnose metabolism. The functional homologue in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. Trifolii is indicated for each gene. *, Homologues involved in rhamno-galacturonan catabolism were identified in Dickeya dadantii 3937. (B) BMC superlocus, compared to GRM3 (21). The functional equivalents in Salmonella Typhimurium of the genes predicted to be involved in the BMC are indicated below each gene. The genes are shown in different colors according to the function of the protein encoded: in blue, enzymes involved in the conversion of propanediol into propionate and propanol; in red, genes predicted to encode BMC-H shell proteins; in purple, genes for BMC-T shell proteins; in orange, genes for BMC-P shell proteins; and in gray, genes with unknown functions.