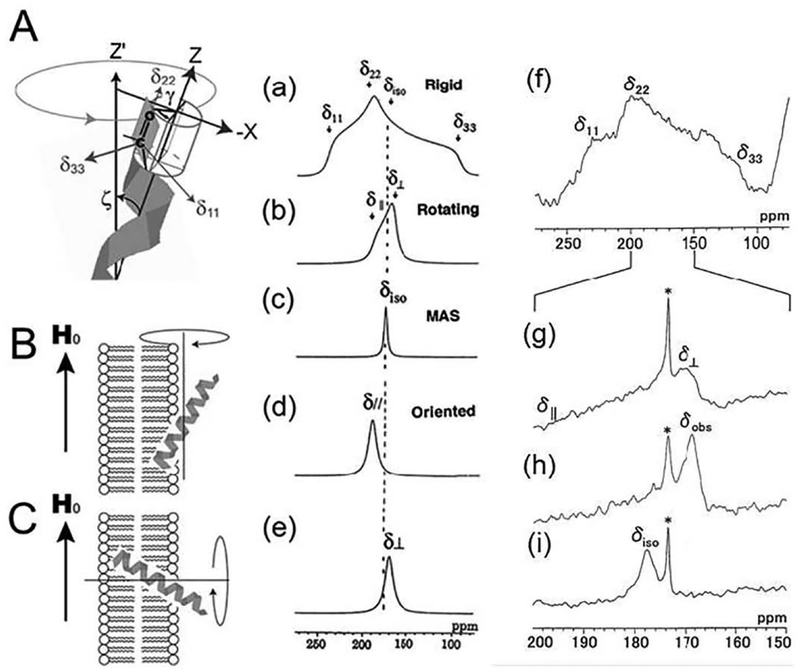
Fig. 1.
A: Direction of the principal axis of the 13C chemical shift tensor of the C=0 group. B: The helical axis rotates about the magnetic field (H0). C: the helical axis rotates about the bilayer normal. 13C NMR spectral patterns of the C=0 carbons corresponding to the orientation of the α-helix with respect to the surface of the magnetically oriented lipid bilayers. Simulated spectra were calculated using δ11 = 241, δ22 = 189, and δ33 = 96 ppm for the rigid case (a), rotation about the unique axis without orienting to the magnetic field (slow MAS condition) (b), MAS (c), rotation about the magnetic field (d), and rotation about the bilayer normal (e). 13C NMR of [1-13C]Ile4-melittin-DMPG bilayer system in the rigid state at − 60 °C (f), in the slow MAS condition at 40 °C (g), in the oriented condition at 40 °C (h), and in the fast MAS condition at 40 °C (i) [12].