FIGURE 1.
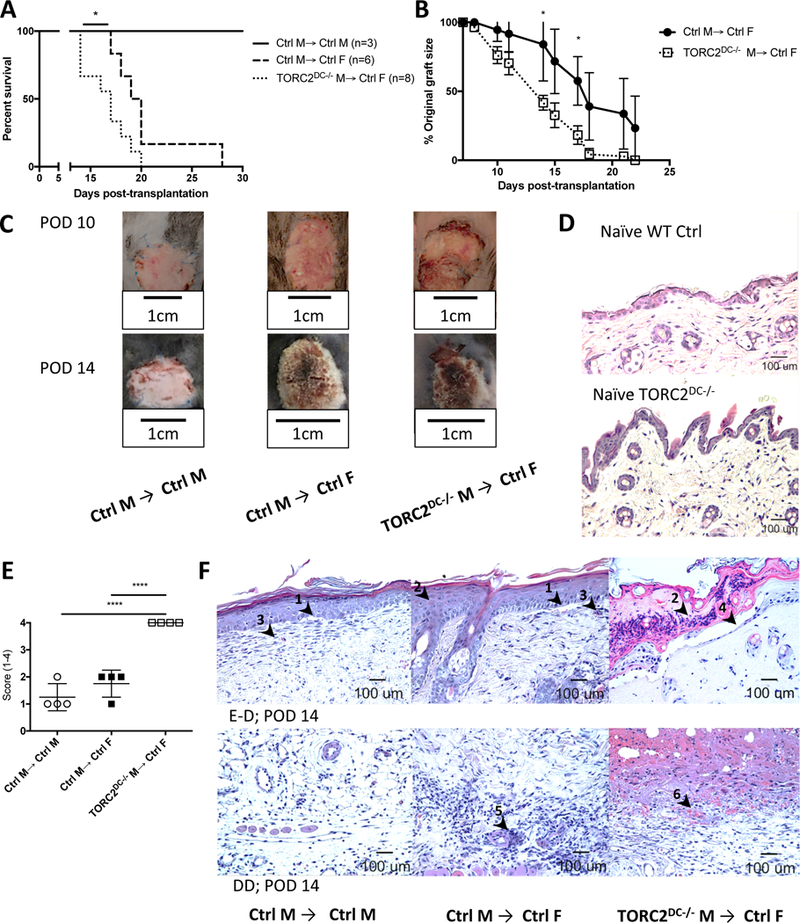
HY-mismatched skin grafts from TORC2DC−/− donors exhibit shortened survival times and enhanced Banff ejection scores. Male (M) or female (F) wild-type B6 mice were transplanted with full-thickness skin grafts from either B6 WT control M (Ctrl M) or B6 TORC2DC−/− M donors. (A) Graft survival over time, n=3–8 mice per group; Log-rank test, *, p < 0.05. (B) Skin graft size as a percentage of original graft size over time, n=6–8 mice per group; Student’s t-test, *, p < 0.05. (C) Representative gross morphology of skin grafts at post-operative day (POD) 10 and POD 14. (D) Representative H&E staining of normal naïve (non-transplanted) WT Ctrl and TORC2DC−/− trunk skin. (E) Banff rejection scores of skin grafts at POD 14, n=4; one-way ANOVA Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, xxxx, p < 0.001. (F) Representative H&E staining of skin grafts at POD 14 showing (above) the epidermal-dermal junction (E-D) and (below) the deep dermal layer (DD). Arrowheads indicate (1) vacuolar damage, (2) pathological diskeratosis, (3) lichenoid infiltrate/interface dermatitis, (4) pemphigoid acantholysis, (5) vasculitis and (6) thrombosis.
