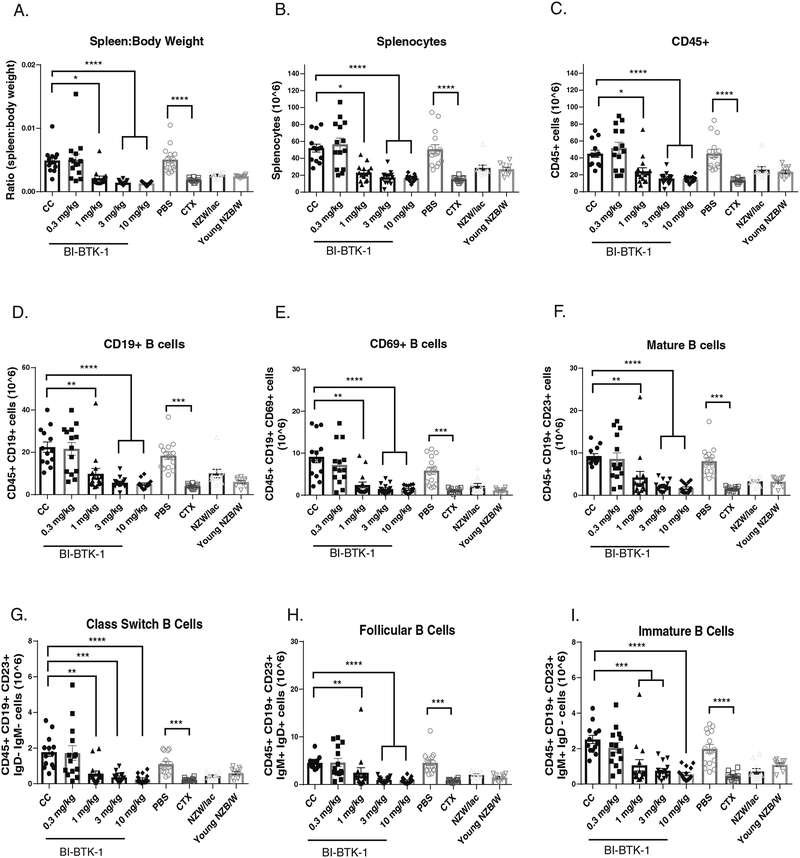
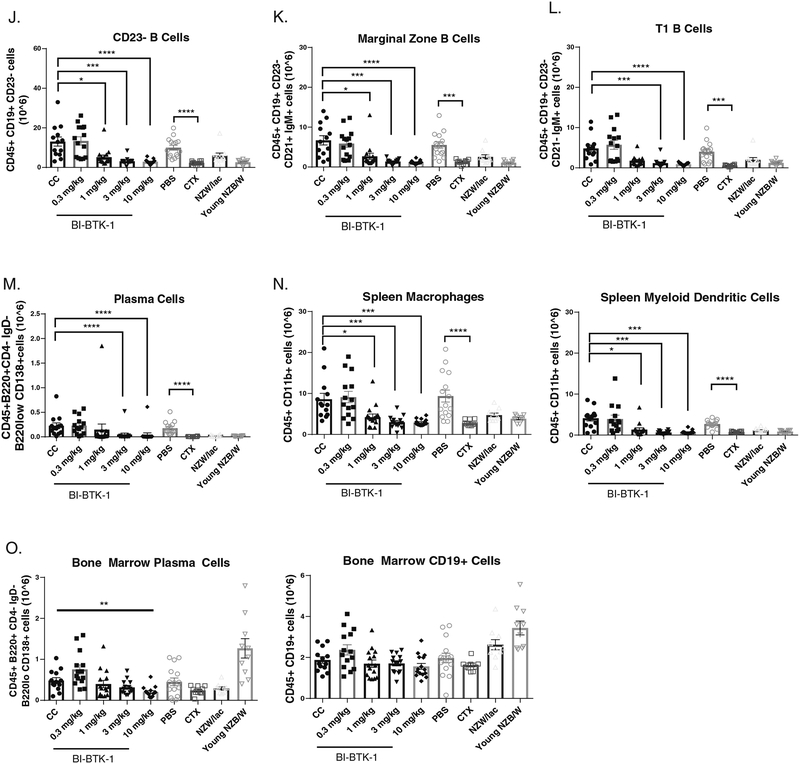
Figure 4. BI-BTK-1 affects multiple B cell subtypes in the spleens of NZB/W mice.
BI-BTK-1 treatment reduced spleen size (A) and total cell numbers within the spleen (B), including total CD45+ cells (C) and, specifically, CD19+ B cells (D). We assessed different B cell subtypes, and found that BI-BTK-1 treatment reduced all tested subsets in a dose responsive manner (E-M). Splenic macrophages and myeloid dendritic cells were also reduced (N). While BI-BTK-1 did not reduce overall B cell numbers in the bone marrow, plasma cell numbers were significantly reduced at the highest dose of 10 mg/kg of BI-BTK-1 compared to control mice (O). (NZB/W mice: CC, n=13; BI-BTK-1: 1 mg/kg, n=15; 3 mg/kg, n=14; 10 mg/kg, n=15; PBS, n=15; CTX, n=10; NZW, n=10; 12 week old NZB/W control, n=10).