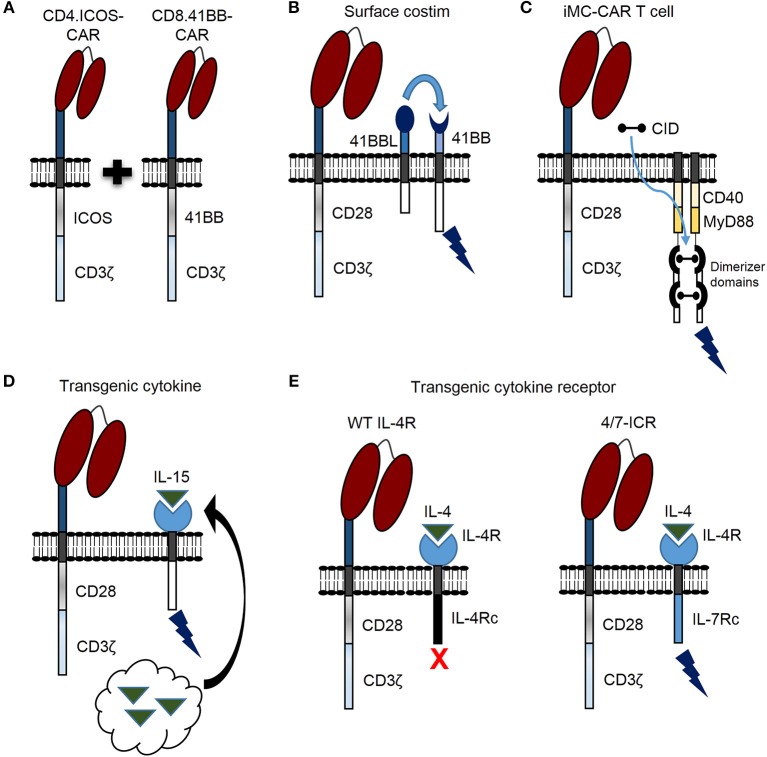
Figure 2.
Novel genetic modifications to enhance CAR T cell persistence against solid tumors. (A) CAR T cell persistence against solid tumors can be enhanced by transducing CD4 and CD8 T cells with different CAR costimulatory domains. (B) CAR T cell activation leads to 41BB receptor (41BB) expression. CAR T cell persistence can be enhanced by constitutive expression of 41BB ligand (41BBL), which interacts with the 41BB receptor in an autocrine or paracrine manner to provide additional costimulatory signal (surface costim). (C) Triggering CAR T cell costimulation with a chemical inducer of dimerization (CID) drug is another promising approach. A molecule, which consists of two dimerizer domains and costimulatory domains derived from MyD88 and CD40 (iMC) can be activated by CID and enhance CAR T cell persistence. (D) Constitutively expressed cytokine (i.e., IL-15) can be engineered by tethering cytokine to the cell membrane (not shown) or secreted by CAR T cells (black arrow) to enhance persistence. (E) The inverted IL-4/IL-7 chimeric cytokine receptor (4/7-ICR) contains an IL-4 receptor extracellular domain (IL-4R) fused to an activating IL-7 cytoplasmic domain (IL-7Rc). While IL-4 binding to wild type (WT) IL-4 receptor leads to CAR T cell inhibition, IL-4 binding to 4/7-ICR enhances persistence and effector function.