FIGURE 3.
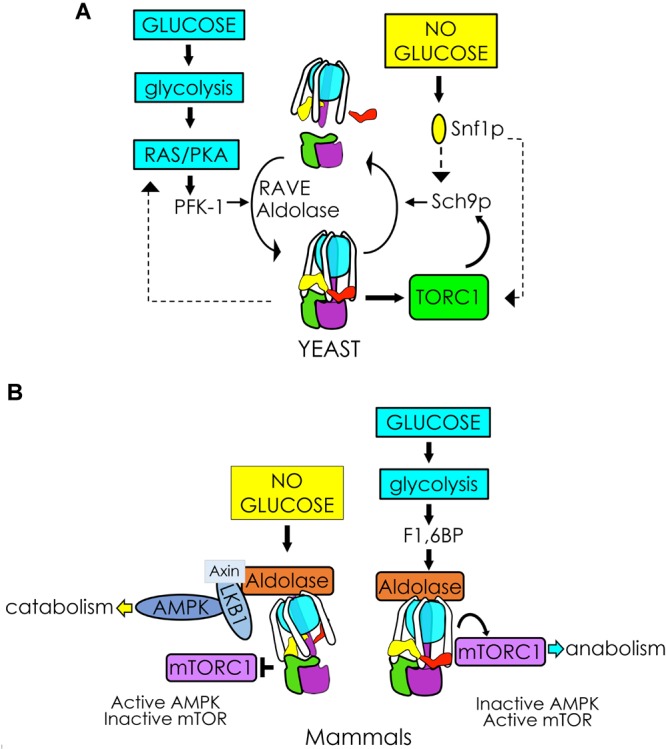
V-ATPase integrates glycolytic signals to control cellular metabolism. (A) In yeast, glycolysis activates RAS/PKA and PFK-1, facilitating V1Vo assembly/activity via RAVE and aldolase. Glucose-induced V-ATPase assembly and PKA activation may function in a positive feedback loop enhancing V1Vo assembly (left). V-ATPase is also necessary for TORC1 phosphorylation of the protein kinase Sch9p, which stimulates metabolism in response to glucose. The V-ATPase-TORC1 interplay is reciprocal. After glucose removal, Snf1p (yeast AMPK) phosphorylates Sch9p, and may participate in a negative feedback response to disassemble V-ATPase (right). (B) In mammals, glucose removal facilitates assembly of a lysosomal AXIN/LKB1/aldolase protein complex to activate AMPK. Activation of AMPK pulls the V-ATPase-Ragulator complex away from mTORC1 and leads to mTORC1 inactivation (left). Glycolytic F1,6BP binds to aldolase, disrupting the lysosomal AMPK activating complex and activating mTORC1 when glucose is available (right).
