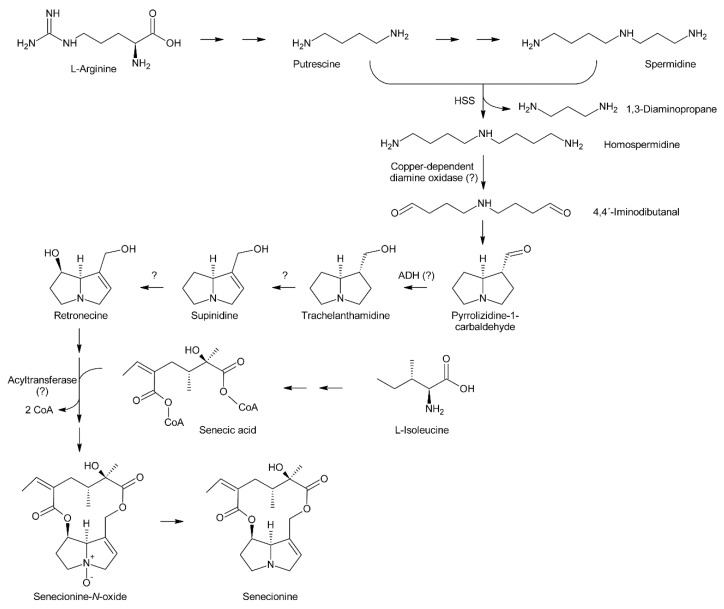
Figure 6.
Biosynthesis of PAs. The polyamines putrescine and spermidine are derived from the basic amino acid arginine. Subsequently, homospermidine synthase (HSS) exchanges the 1,3-diamonopropane residue of spermidine by putrescine, which releases 1,3-diaminopropane and forms symmetric homospermidine. Oxidation of homospermidine, likely by copper-dependent diamine oxidases, to 4,4´-iminodibutanal initiates cyclization to pyrrolizidine-1-carbaldehyde, which is reduced, likely by an alcohol dehydrogenase, to 1-hydroxymethylpyrrolizidine. Desaturation and hydroxylation by unknown enzymes form retronecine, which is acylated with an activated necic acid, for instance with senecyl-CoA2 as in the example shown above. Acylation might be catalyzed by an acyltransferase of the BAHD family. PA N-oxides, which are believed to be the primary products of PA biosynthesis, may be reduced to the free tertiary amine.