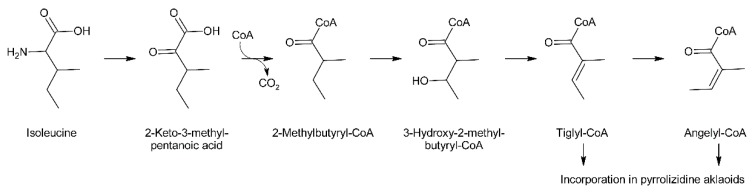
Figure 11.
Biosynthesis of tiglic and angelic acid. l-Isoleucine is desaminated and the obtained ketocarboxylic acid decarboxylated to 2-methylbutyric acid, which is likely accompanied by linking with coenzyme A to yield 2-methylbutyryl-CoA. This intermediate is hydroxylated and subsequently dehydrated to form tiglyl-CoA, which can be isomerized to angelyl-CoA. The activated tiglic and angelic acid residues are finally transferred to necine bases and coenzyme A is released.