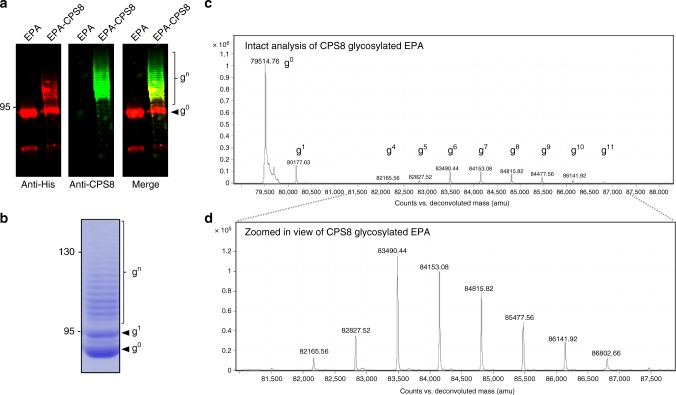
Fig. 6.
Analysis of exotoxin A from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (EPA) glycosylation with the CPS8 capsular polysaccharide. Western blot analysis of EPA-CPS8 bioconjugates compared against EPA alone. a(Left panel Anti-His channel probing for Hexa-histidine-tagged EPA purified from SDB1 expressing CPS8 in the presence or absence of PglS. a (Middle panel) Anti-glycan channel probing for CPS8. a (Right panel) Merged images for left and middle panels. b EPA-CPS8 separated on a SDS- polyacrylamide gel stained with Coomassie. c, d Intact protein mass spectrometry analysis showing the MS1 mass spectra for purified EPA-CPS8. The EPA fusion protein has a theoretical mass of 79,526.15Da and can be observed as the peak at 79,514.76 Da. The EPA fusion protein was also observed in multiple states of increasing mass corresponding to the CPS8 repeating subunit, which has a theoretical mass of 662Da. Varying glycoforms of the EPA-CPS8 were observed and are denoted by “gnumeric”, where “g” stands for glycoform and the “numeric” corresponds to the number of repeating CPS8 subunits. The EPA fusion protein was modified with up to 11 repeating subunits of the CPS8 glycan. Panel d provides a zoomed in view of the varying EPA-CPS8 glycoforms. Source data are provided as a Source Data file