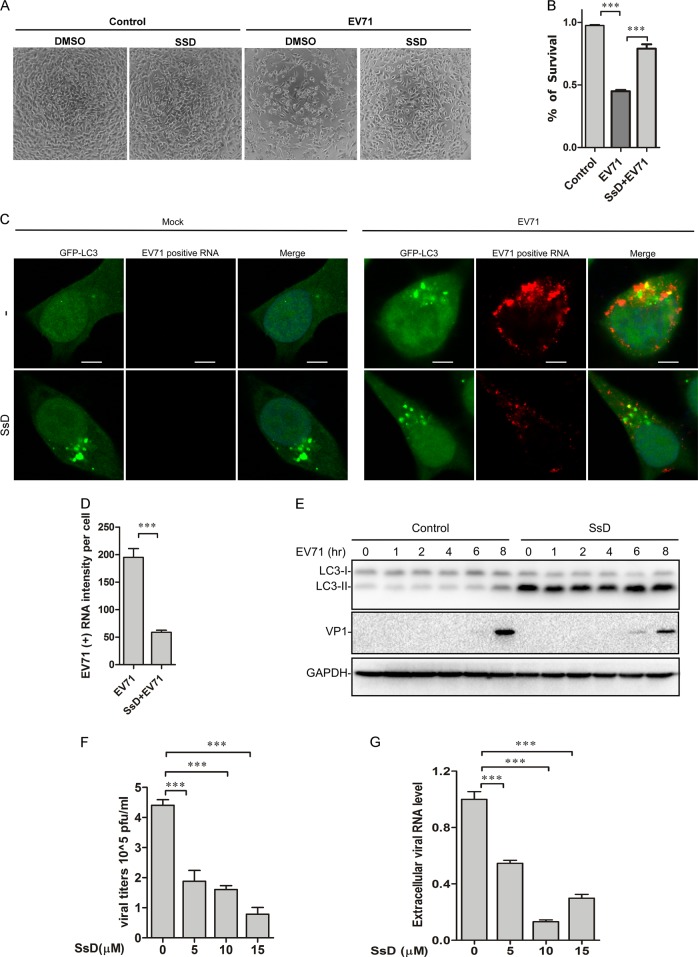
Fig. 6.
SsD inhibits EV-A71 replication in HeLa cells. a HeLa cells pretreated with or without SsD (15 μM) were infected with EV-A71 (MOI = 1) for 12 h. SsD pretreatment greatly reduced the number of cytopathic cells after EV-A71 infection. b HeLa cells were infected with EV-A71 (MOI = 1) in the presence or absence of SsD (15 μM) for 12 h, and MTT assays were performed. The graph represents data from three independent experiments, and data are expressed as the mean ± S.D., n = 3. The asterisk (*) symbols indicate p < 0.05 by t test analysis. c and d GFP-LC3-expressing HeLa cells were infected with EV-A71 (MOI = 1) in the presence or absence of SsD (15 μM) for 5 h, and EV-A71 positive strand RNA hybridization was performed (c). Quantification of EV-A71 positive RNA intensity per cell is expressed as the mean ± S.E., n = ~50 cells from 3 independent experiments. The asterisk (*) symbols indicate P < 0.05 by Student’s t Test analysis (d). e HeLa cells were infected with EV-A71 (MOI = 1) in the presence or absence of SsD (15 μM) for the indicated times, followed by LC3, VP1, and GAPDH immunoblot analyses. f Viral titers were significantly decreased by SsD treatment in a dose-dependent manner after EV-A71 infection. WT HeLa cells were infected with EV-A71 (MOI = 1) for 12 h. g SsD (15 μM) treatment markedly reduced extracellular EV-A71 RNA level in a dose-dependent manner. WT HeLa cells were infected with EV-A71 (MOI = 1) for 12 h