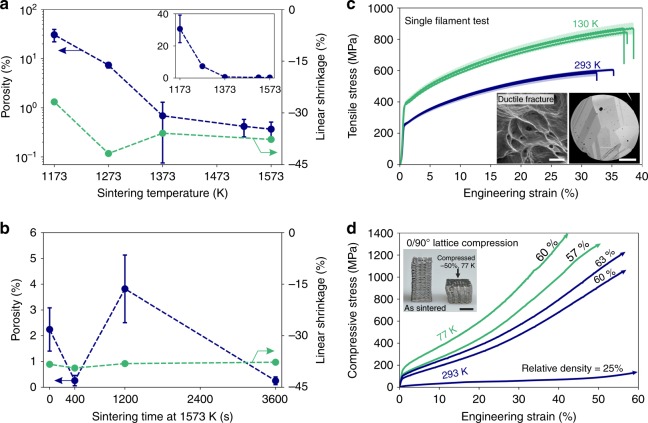
Fig. 4.
Porosity evolution and mechanical performance of extrusion-printed 250 µm CoCrFeNi HEA filaments. a Evolution of porosity (logarithmic scale, blue) and shrinkage (linear scale, green) with increasing sintering temperature in H2 for 1 h dwell time. Extensive, reproducible linear shrinkage is observed, with a maximum at 1273 K. Averaged data over all nozzle diameters. Inset: Porosity on a linear scale for comparison. Error bars correspond to ± σ. b Evolution of porosity and shrinkage (both linear scale) with sintering time at 1573 K in H2. Error bars correspond to ±σ. c Engineering stress-strain curves of single filaments (125 µm average diameter, 10 mm gauge length, from 250 µm nozzle, sintered at 1573 K/1 h) tested in tension at 130 K (green line) and 293 K (blue line) until fracture. Shading corresponds to the 1σ error in calculated stress based on the measured cross-sectional area variation of filaments. Inset: fracture surface showing dimples typical of ductile fracture mode at 293 K (scale bar 1 µm) and cross-section of a filament showing its oligocrystalline structure (grain size: 35–80 µm). Scale bar is 25 µm. d Compressive stress-strain curve of 0/90° cross-ply CoCrFeNi HEA micro-lattices with 25% (when extruded with a 200 µm nozzle) to 63% (250 µm nozzle) relative density, sintered at 1573 K for 1 h, and tested at 77 K (green) and 293 K (blue), showing extensive plastic deformation at all temperatures. All tests were interrupted prior to fracture. Inset: Sintered lattice before (left) and after (right) compression to −50% at 77 K, showing homogeneous deformation. Scale bar is 2 mm