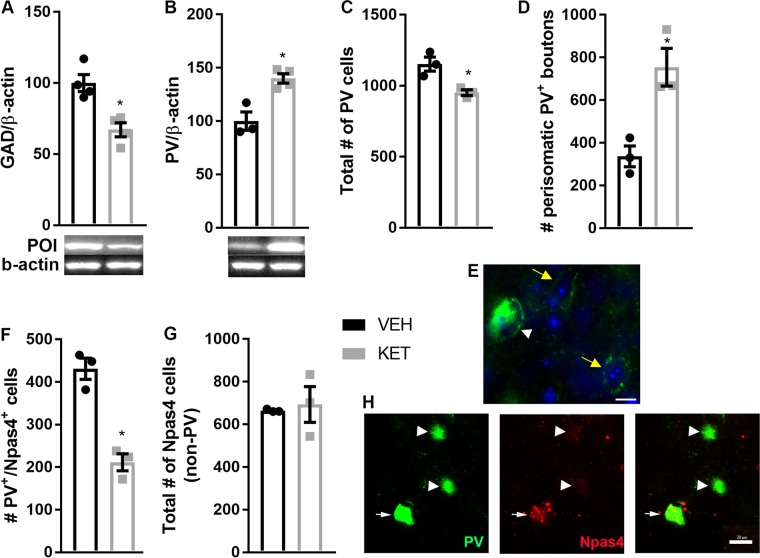
Fig. 2. Mice neonatally exposed to the NMDA receptor antagonist ketamine (KET mice) show downregulation of Npas4 specifically in PV-I of the PFC.
a, b Adult KET mice have decreased protein levels of GAD67 (t6 = 4.266; p = 0.005) and increased protein levels of PV (unpaired t-test: t5 = 4.466; p = 0.007) in the PFC when compared to VEH control mice. c KET mice have less PV+ somata in their PFC compared to VEH control mice (t4 = 3.779; p = 0.019). d KET mice have more PV+ boutons in their PFC compared to VEH control mice (t4 = 4.142; p = 0.014). e Representative picture of PV+ somata (white arrow head) and PV+ boutons (yellow arrows); PV is green, DAPI is blue. f KET mice have less PV+ cells expressing Npas4 (t4 = 6.871; p = 0.002), but (g) no change in the number of Npas4-expressing cells outside PV+ neurons (p > 0.05). h Representative pictures of immunofluorescence staining for PV (green) and Npas4 (red). Arrow points to a double stained cell (PV+ neurons expressing Npas4), while arrowheads point toward PV+ neurons not expressing Npas4. *p ≤ 0.05; VEH n = 3–4; KET n = 4; POI = protein of interest. Scale bar = 20 µm