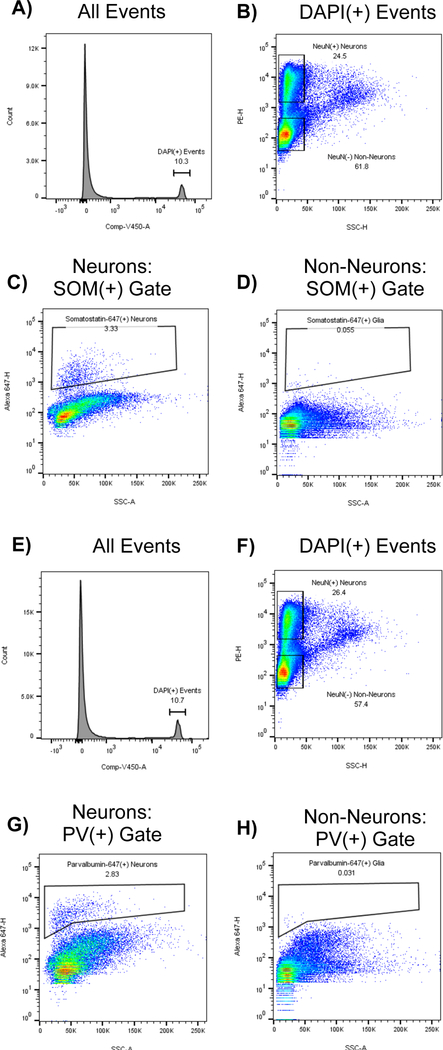
Figure 3: Specific staining for interneuron markers somatostatin and parvalbumin is largely absent from non-neuronal populations:
As a control, somatosensory cortex was fixed in paraformaldehyde, dissociated, split into two aliquots, and stained with DAPI, NeuN-PE, and either somatostatin-647 (A-D) or parvalbumin-647 (E-H). Top 4 panels (A-D) show the gating strategy for tissue stained for somatostatin: A) DAPI(+) events are gated B) Neurons and Non-Neurons are gated based on NeuN-PE signal, but excluding events with high SSC-H. C) Somatostatin(+) gate drawn on the NeuN(+) population. D) Somatostatin(+) gate drawn on NeuN(−) population. Note that neurons contain a distinct subpopulation of somatostatin(+) events, while nonneurons do not. Botttom 4 panels (E-H) show the gating strategy for tissue stained for parvalbumin: E) DAPI(+) events are gated F) Neurons and Non-Neurons are gated based on NeuN-PE signal, but excluding events with high SSC-H. G) Parvalbumin(+) gate drawn on the NeuN(+) population. H) Parvalbumin(+) gate drawn on the NeuN(−) population. Note that neurons contain a distinct subpopulation of parvalbumin(+) events, while nonneurons do not.