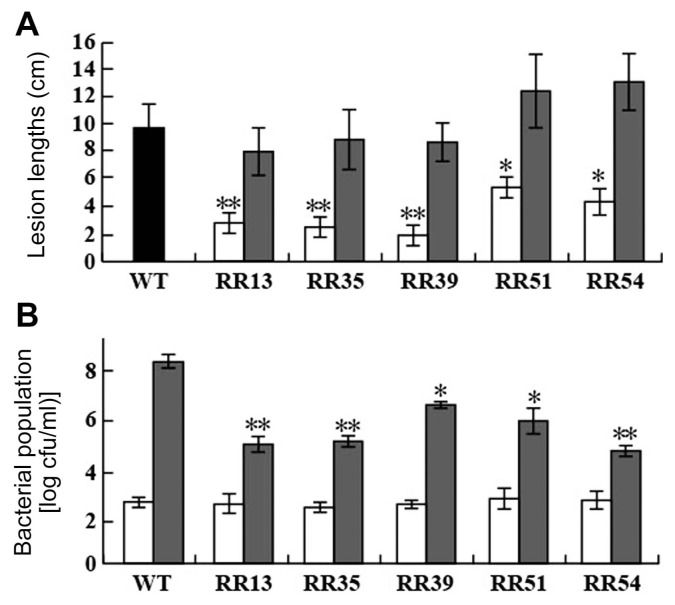
Fig. 1.
Virulence phenotypes of PXO99A (WT) and RR mutant strains. (A) Lesion lengths caused by PXO99A (WT, black), RR mutant (white), and the complementary (gray) strains on Dongjin rice leaves at 14 days after infection (DAI). Rice leaves were infected with 107 cfu/ml of bacterial suspension by the scissor clipping method. Bars are mean ± SD (n = 20). * or ** indicate that the lesion length of each mutant was significantly different from that of PXO99A by Duncan’s test (P < 0.05). (B) Bacterial population at 0 (white) and 14 (gray) DAI. Immediately after infection (0 DAI) and at 14 DAI, 1-cm2 and 25-cm2 samples from the infected site of three leaves were used to extract the bacteria population at 0 and 14 dpi, respectively. Bars are mean ± SD (n = 3). * and ** indicate that the population of mutants was significantly smaller than that of PXO99A by Duncan’s test (P < 0.05). C) All experiments were repeated three times with high consistency, and the results from one experiment are shown.