Figure 2: Activating LC-GABA neurons reduces LC-NA mediated pupil size.
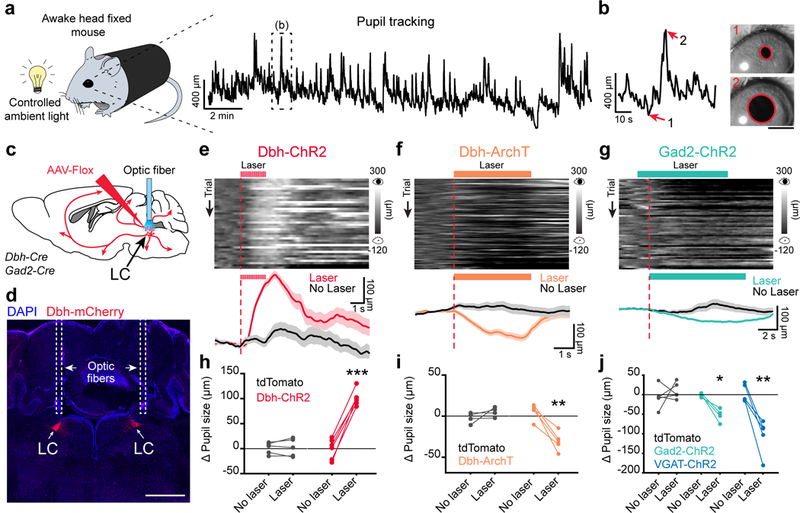
a. Methods to measure pupil size in awake head-fixed mice using a CMOS camera and infrared illumination. Right: pupil diameter for an example 20-minute session. Boxed area is expanded in (b). b. Example images of pupil tracking for constricted (1) and dilated epochs (2). Scale bar: 1 mm. c. Methods for optogenetics manipulation of LC-NA and LC-GABA neurons using Cre-dependent viruses, Dbh- and Gad2-Cre mice and fiber optic implantation. d. Coronal section of the LC showing ChR2-mCherry expression and optic fiber tracks in a Dbh-Cre mice. Scale bar: 1 mm. e – g. Effect of activating (Dbh-ChR2) or silencing (Dbh-ArchT) LC-NA neurons as well as activating LC-GABA neurons (Gad2-ChR2) on pupil size in example mice. Top panels – Temporal raster plots of pupil size aligned to optical activation onset (vertical red line). Bottom panels – session averages for trials with and without laser. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. h - j – Effect of activating or silencing LC-NA neurons as well as activating LC-GABA neurons on pupil size. Gray lines represent animals where only tdTomato was expressed, but similar optical activation patterns and intensities were used. N = 6, 5, 4 and 5 mice for Dbh-ChR2, ArchT, Gad2-ChR2 and VGAT-ChR2 conditions respectively. N = 5 mice for tdTomato controls. Paired two-tailed t-test with p = 0.822 (t4 = 0.240) and ***p = 0.00001 (t5 =14.553) for tdTomato and ChR2 conditions in (h); p = 0.249 (t3 = 1.426) and **p = 0.0045 (t4 = −5.768) for tdTomato and ArchT conditions in (i); p = 0.4747 (t4 = 0.788), **p = 0.0054 (t4 = −5.494) and *p = 0.0153 (t3 = −5.010) for tdTomato, VGAT-ChR2 and Gad2-ChR2 conditions in (j).
