Figure 3.
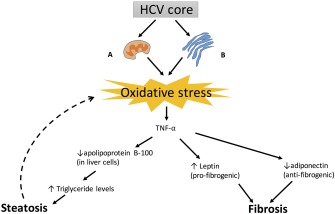
(A) At the mitochondria of hepatocytes, HCV core protein promotes intracellular calcium, which increases the reactive oxygen species (ROS) production through the electron transport chain. (B) At the ER of hepatocytes there is viral replication causing assembly chaperones to be overloaded, and misfolded proteins lead to ER dysfunction and increased ROS. The oxidative stress of HCV leads to triglyceride accumulation within hepatocytes by upregulating apolipoprotein B‐100, causing a cycle of steatosis and more oxidative stress. Leptin is also upregulated and adiponectin downregulated, eventually leading to fibrosis of the liver.
