Figure 6.
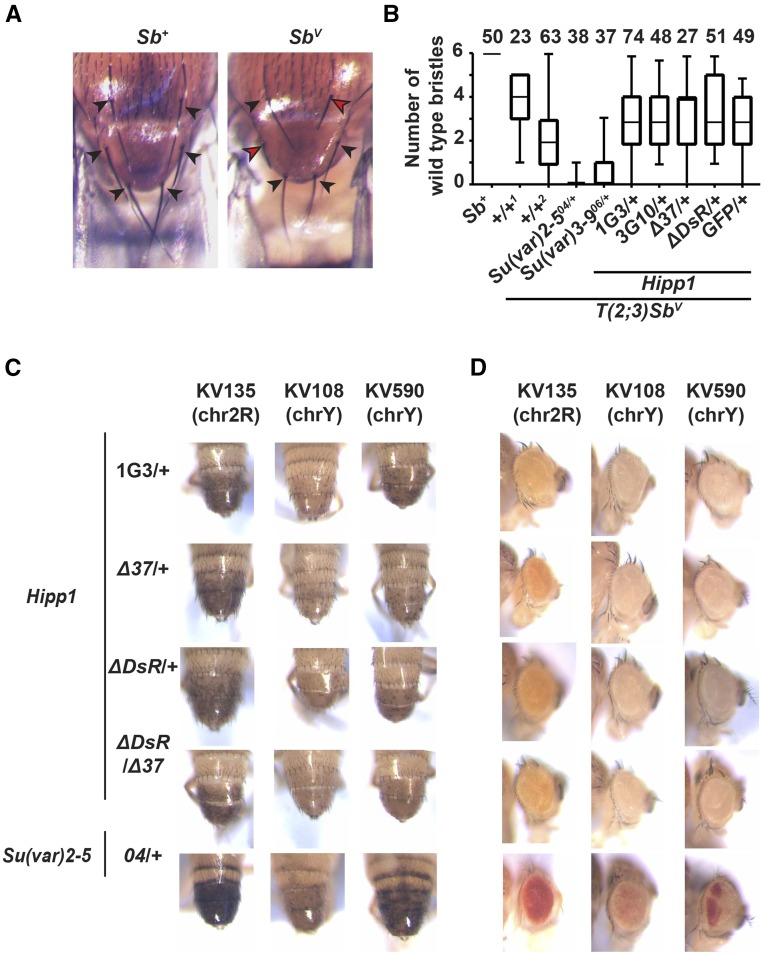
HIPP1 is not essential for HP1a-associated transcriptional silencing. A. Images of the thorax in a Sb+ (Canton S) and a SbV animal, illustrating the six thoracic bristles that were quantified as either long (black arrowhead) or short (red arrowhead). B. Box plots of quantification of the number of long bristles per thorax of female progeny resulting from crosses of wild type females (Sb+/+, Canton S) or Sbv/+ females with males that have no modifier mutations (1, Canton S; 2, yw), males with known modifier mutations [Su(var)2-504, Su(var)3-906], or with Hipp1 mutant males of the indicated genotypes. The number of individuals scored is shown above each bar. Each box represents the 25th to 75th percentile interval, the line represents the median, and the whiskers represent the range. C. D. Images of abdominal body (C) or eye (D) pigmentation from representative males carrying heterochromatic SUPorP insertions crossed into a reference background expressing full length HIPP1 (Hipp1G3/+), as well as mutant backgrounds heterozygous or homozygous loss of HIPP1 or HP1a [Su(var)2-504]. Phenotypes of newly eclosed males were determined. Shown are males represent the median level of pigmentation within a randomly selected collection.