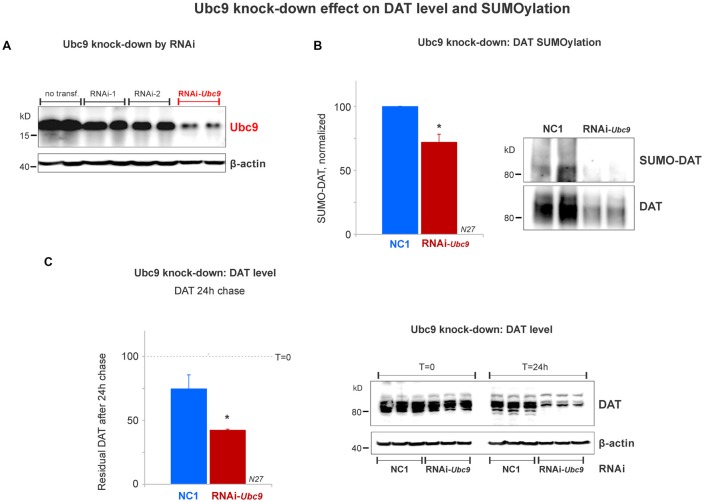
Figure 5.
Ubc9 knock-down by interference RNA (RNAi) decreases DAT SUMOylation and enhances DAT degradation in N27 cells. (A) The combined RNAi-1 and -2 (RNAi-Ubc9) substantially reduced the level of endogenous Ubc9, compared with controls (no transfection or each individual RNAi construct). (B) Ubc9 knock-down by RNAi-Ubc9 decreases DAT SUMOylation when compared with NC1 (control). DAT was immunoprecipitated with anti-DAT (EL2) and detected by anti-DAT (MAB) antibodies, followed by the detection of SUMO-DAT with mouse anti-SUMO1 antibody. The normalized value of SUMO-DAT corresponds to the ratio of SUMO-DAT/DAT (three independent experiments). (C) In the 24 h chase study, Ubc9 knock-down reduces the residual level of endogenous DAT, which is derived from enhanced DAT degradation, compared with control (NC1). DAT was detected using anti-DAT (EL2) antibody (top) and the β-actin loading control is shown at the bottom. Values are presented as the average of the remaining fraction (T = 24 h) from the initial amount (100%, T = 0). Data represent mean ± SE. Statistical significance from normalized control (*p < 0.05) was determined by a two-sided, Student’s t-test (three independent experiments).