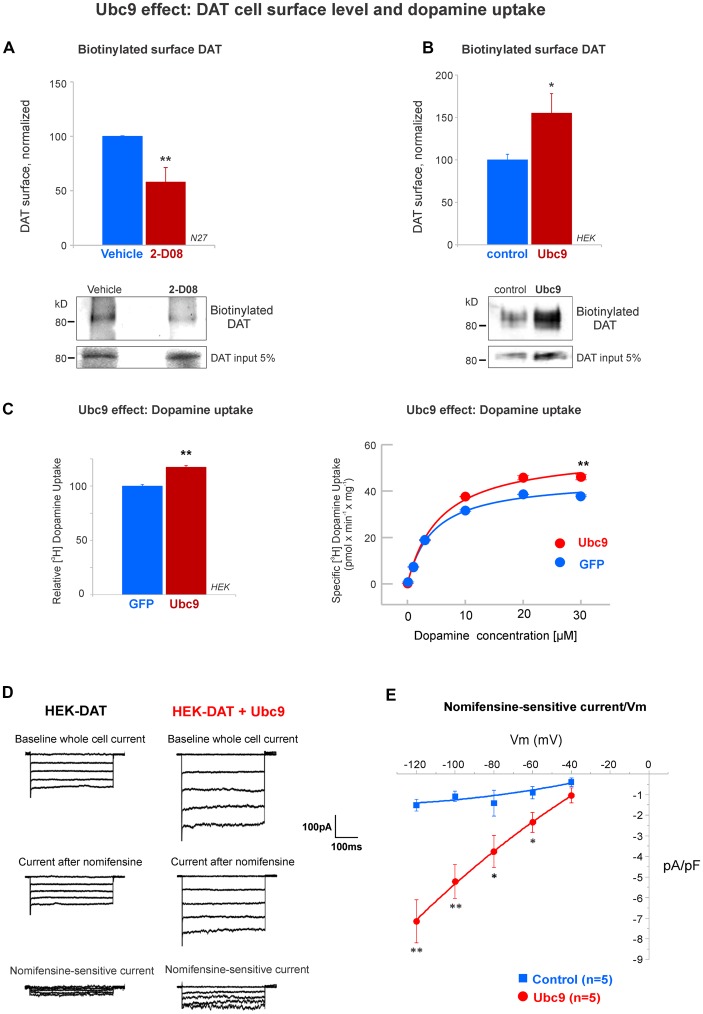
Figure 9.
Ubc9 enhances the functional level of DAT in the plasma membrane. (A) The Ubc9 inhibitor 2-D08 significantly reduces the surface level of DAT in N27 cells. Surface biotinylated DAT was immunoblotted with anti-DAT (MAB) antibody, including DAT 5% input (four independent experiments). (B) Surface biotinylated DAT level was significantly increased with Ubc9 overexpression in HEK-DAT cells. Values were normalized as average ± SE (six independent experiments). (C) Dopamine uptake is enhanced by Ubc9-GFP overexpression in HEK-DAT cells. Left, Ubc9 increases the maximum uptake of relative 3,4-[7-3H] dihydroxy-phenylethylamine ([3H]-dopamine) in comparison to GFP control cells. Non-specific dopamine uptake was determined in the treatment of 0.01 mM GBR12935 or 1 mM dopamine (five independent experiments). Right, representative saturation curve of [3H]-dopamine uptake in HEK293-DAT cells transfected with GFP or Ubc9-GFP. The overexpression of Ubc9 resulted in an increase in the maximum specific dopamine uptake velocity without a change in the affinity for dopamine. (D) Ubc9-GFP increases DAT-mediated uncoupled currents. HEK-DAT cells were voltage clamped in the whole cell configuration, 24–36 h after transfection, while the membrane potential was stepped from −120 to −40 mV from a holding potential of −40 mV in 20 mV increments. Representative traces of whole cells and nomifensine-sensitive uncoupled DAT currents are shown (three independent experiments). (E) Nomifensine sensitive currents were plotted in a current-voltage relationship. All values are shown as average ± SE and statistical significance (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01) was determined by a two-sided Student’s t-test.