Fig 6. SIRT1 is required for the beneficial effects of NAMPT on ethanol-induced hepatic steatosis and injury.
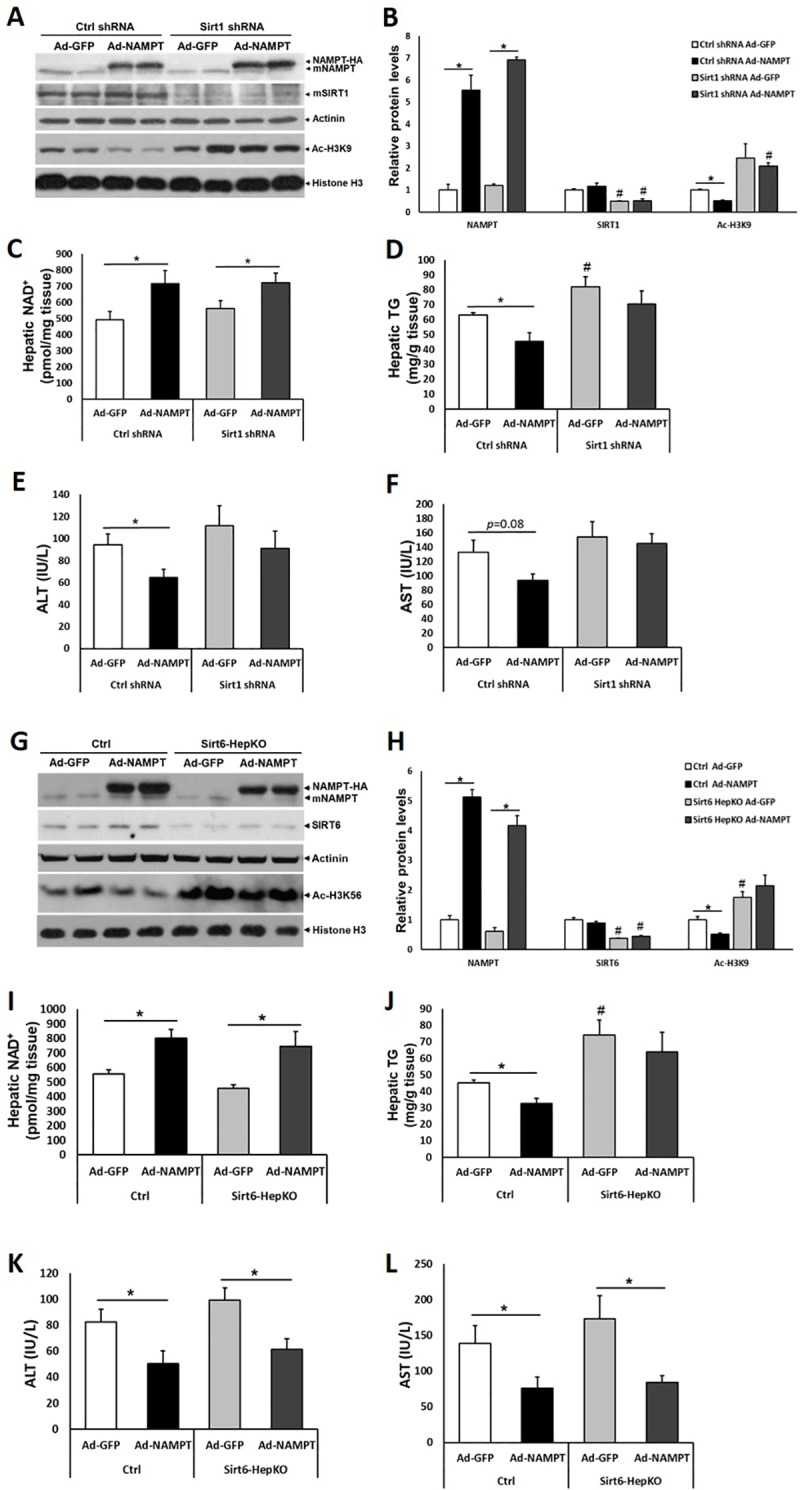
Mice were fed with ethanol diet as described in Fig 3; adenovirus treatments were performed as in Fig 4. (A) Adenovirus-mediated Sirt1 shRNA and NAMPT-HA expression as well as histone H3K9 acetylation levels were examined by western blot. (B) Densitometric analysis of the immunoblot data in Panel A. (C and D) NAD+ (C) and TG (D) concentrations were examined in mouse liver tissues. (E and F) Serum ALT (E), AST (F) levels were analyzed. (G) Adenovirus-mediated NAMPT-HA expression as well as protein levels of SIRT6 and Ac-H3K56 were examined by western blot. (H) Densitometric analysis of the immunoblot data in Panel G. (I and J) NAD+ (I) and TG (J) concentrations were examined in mouse liver tissues. (K and L) Serum ALT (K), AST (L) levels were analyzed. Data are shown as mean ± S.E.M (n = 5–6 for each group). *p < 0.05 for Ad-GFP vs Ad-NAMPT; #p < 0.05 vs Ctrl shRNA Ad-GFP in Panel B and D; #p < 0.05 vs Ctrl Ad-GFP in Panel H and J.
