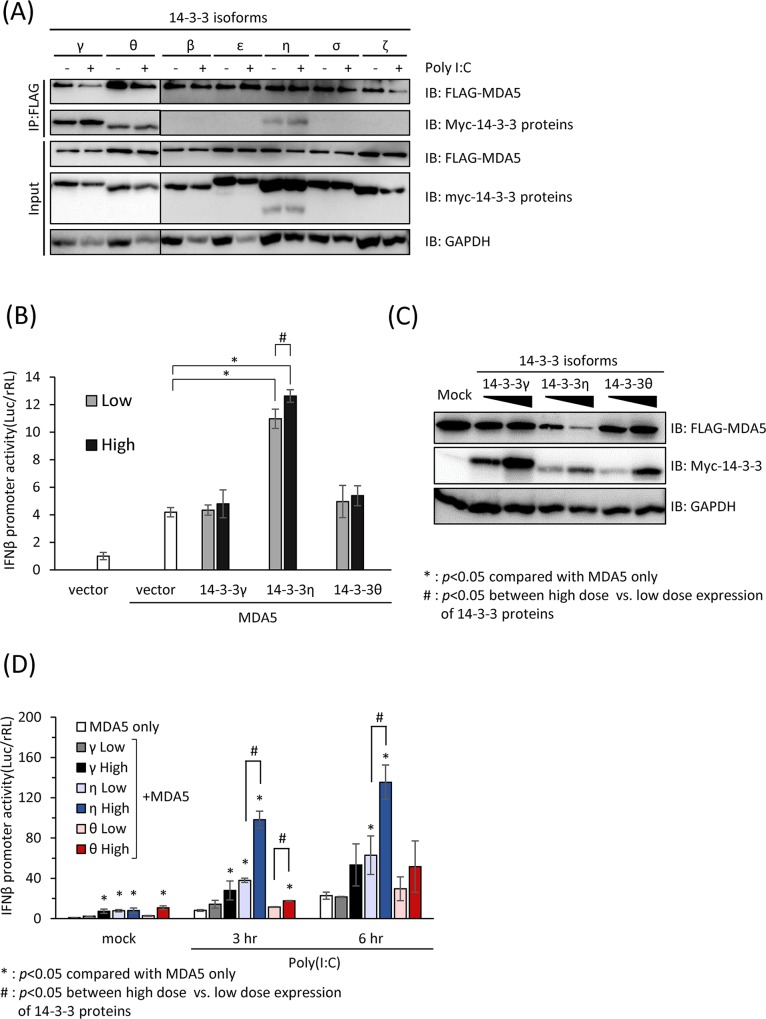
Fig 2. 14-3-3η interacts with MDA5 and promotes MDA5-dependent antiviral signaling pathway.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation assay of MDA5 and various 14-3-3 isoforms. Huh7 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged full-length MDA5 with different isoforms of myc-tagged 14-3-3 proteins and subsequently stimulated with 1μg/mL poly (I:C) for 6 hours or leaved unstimulated (mock). Cell lysates were then subject to anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation. Asterisks indicate non-specific bands. (B) Increasing doses of myc-tagged 14-3-3γ, 14-3-3η and 14-3-3θ and a constant amount of FLAG-MDA5 were co-transfected into RG-I K/D Huh7 cells. The IFNβ promoter activities driven by the ectopic expression of MDA5 alone with 14-3-3γ, 14-3-3η and 14-3-3θ were detected by dual luciferase assay. Ectopic expressed 14-3-3η significantly increased the IFNβ promoter activities driven by MDA5 expression. *: p<0.05, when compared with MDA5 only. (C) Protein expression levels of figure (B) by immunoblotting. (D) MDA5 alone or MDA5 with increasing doses of myc-tagged 14-3-3γ, 14-3-3η and 14-3-3θ were transfected into the RIG-I K/D Huh7 cells. The transfected cells were subsequently stimulated with 1 μg/mL of poly(I:C) for 3 to 6 hours. The IFNβ promoter activities were detected by dual luciferase assay. *: p<0.05, when compared with MDA5 only at the same time point. #: p<0.05, when IFNβ promoter activities in high and low 14-3-3 expressing cells of the same isoform are compared.