Figure 2: Various types of internal protein motions.
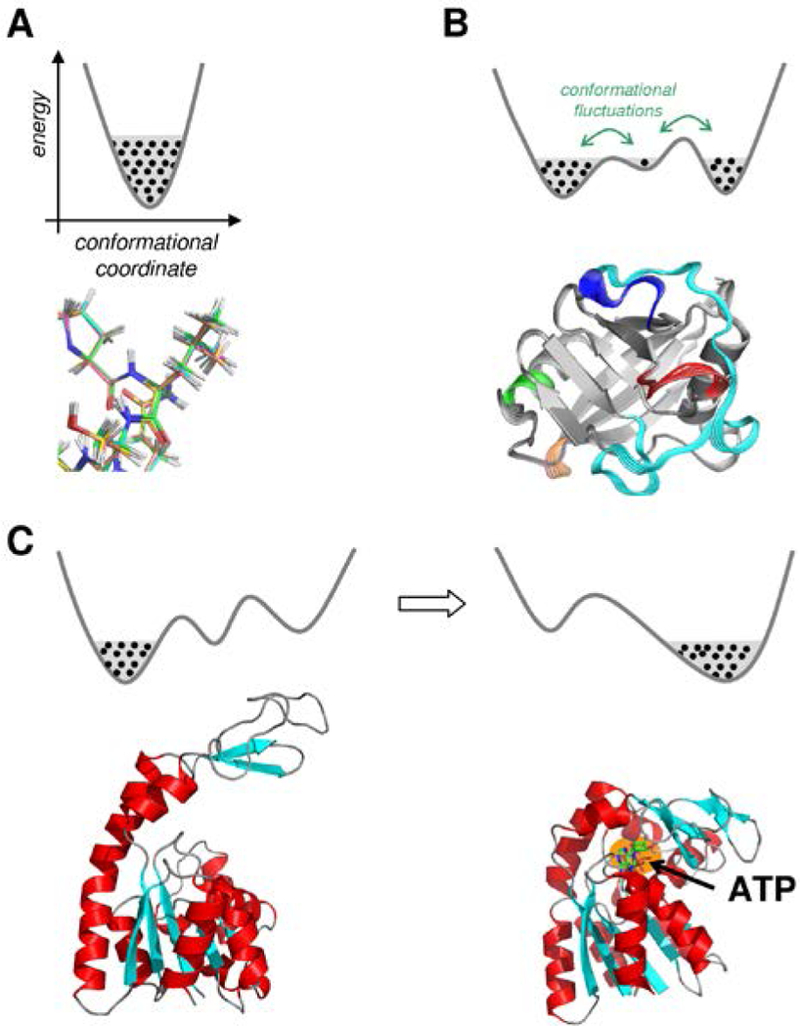
(A) Fast motions. Each black dot indicates a unique conformation. (B) The conformational fluctuations correspond to large scale movements within protein domains or entire protein. These types of motions allow sampling large areas of conformational landscape that could span over multiple minima. (C) Structural changes are induced by events such as binding (or release) of other molecules. Shown here is the enzyme adenylate kinase in the apo form (left) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) bound (right).
